

过程工程学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (7): 774-785.DOI: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.220229CSTR: 32067.14.jproeng.220229
吴秋莹1,2( ), 孔令凯2,3, 徐骥2,4(
), 孔令凯2,3, 徐骥2,4( ), 葛蔚2,3,4, 袁绍军1(
), 葛蔚2,3,4, 袁绍军1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-07-20
修回日期:2020-08-07
出版日期:2021-07-28
发布日期:2021-07-27
作者简介:吴秋莹(1995-),女,四川省资阳市人,硕士研究生,化学工程,E-mail: qywu@ipe.ac.cn;通讯联系人基金资助:
Qiuying WU1,2( ), Lingkai KONG2,3, Ji XU2,4(
), Lingkai KONG2,3, Ji XU2,4( ), Wei GE2,3,4, Shaojun YUAN1(
), Wei GE2,3,4, Shaojun YUAN1( )
)
Received:2020-07-20
Revised:2020-08-07
Online:2021-07-28
Published:2021-07-27
摘要:
气固流态化过程中流体和颗粒分别聚集,形成稀密两相,严重限制其传质效率和反应速率的提高。针对此问题,本工作设计了一种中空多孔结构的催化剂颗粒,通过模拟方法研究该颗粒对稀密两相气相传质与反应的影响,及其在稀密相间转换的时间尺度。结果表明,一定的流动强度时,在颗粒稀密相转换的时间尺度内,中空多孔结构的颗粒能够有效地在稀相存储反应气体,并在密相释放,为密相提供额外的反应气体,增强体系的整体反应效率。当催化反应速率高于传质速率时,在所研究的流动条件下中空多孔颗粒体系的反应效率比实心球形颗粒体系高出26.92%~29.55%。可以预见在稀密相分布更广的大型气固流化床反应器中,中空多孔结构的催化剂颗粒能够更为有效地提高反应器的整体效率。
中图分类号:
吴秋莹, 孔令凯, 徐骥, 葛蔚, 袁绍军. 气固两相流内中空多孔催化剂性能的数值模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(7): 774-785.
Qiuying WU, Lingkai KONG, Ji XU, Wei GE, Shaojun YUAN. Numerical simulation of hollow catalyst with pores in gas-solid reaction system[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2021, 21(7): 774-785.
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Particle diameter/m | 5.0×10-3 |
| Grid size/m | 5.0×10-4~2.0×10-3 |
| Time step/s | 2.0×10-5~5.0×10-5 |
| Inlet mass fraction of A | 1.0 |
| Inlet mass fraction of B | 0.0 |
| Inlet mass fraction of I | 0.0 |
表1 模拟参数
Table 1 Parameters of numerical simulation
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Particle diameter/m | 5.0×10-3 |
| Grid size/m | 5.0×10-4~2.0×10-3 |
| Time step/s | 2.0×10-5~5.0×10-5 |
| Inlet mass fraction of A | 1.0 |
| Inlet mass fraction of B | 0.0 |
| Inlet mass fraction of I | 0.0 |
| Res | Frössling | Ranz-Marshall | Lu et al[ | Simulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 3.75 | 3.90 | 3.68 | 3.80 |
| 20 | 4.47 | 4.68 | 4.51 | 4.79 |
| 40 | 5.49 | 5.79 | 5.67 | 6.14 |
| 60 | 6.28 | 6.65 | 6.56 | 7.16 |
| 100 | 7.52 | 8.00 | 7.94 | 8.51 |
| 200 | 9.81 | 10.49 | 10.46 | 11.31 |
表2 单个实心球形催化剂的颗粒舍伍德数
Table 2 Particle Sherwood number (Shs) of the single solid spherical catalyst
| Res | Frössling | Ranz-Marshall | Lu et al[ | Simulation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 3.75 | 3.90 | 3.68 | 3.80 |
| 20 | 4.47 | 4.68 | 4.51 | 4.79 |
| 40 | 5.49 | 5.79 | 5.67 | 6.14 |
| 60 | 6.28 | 6.65 | 6.56 | 7.16 |
| 100 | 7.52 | 8.00 | 7.94 | 8.51 |
| 200 | 9.81 | 10.49 | 10.46 | 11.31 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Particle diameter/m | 1.0×10-4 |
| Grid size/m | 1.0×10-5~5.0×10-5 |
| Time step/s | 1.0×10-7 |
| Inlet mass fraction of A | 0.9 |
| Inlet mass fraction of B | 0.0 |
| Inlet mass fraction of I | 0.1 |
表3 稀相体系模拟参数设置
Table 3 Parameters of numerical simulation in dilute phase
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Particle diameter/m | 1.0×10-4 |
| Grid size/m | 1.0×10-5~5.0×10-5 |
| Time step/s | 1.0×10-7 |
| Inlet mass fraction of A | 0.9 |
| Inlet mass fraction of B | 0.0 |
| Inlet mass fraction of I | 0.1 |
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Particle diameter/m | 1.0×10-4 |
| Grid size/m | 1.0×10-5~5.0×10-5 |
| Time step/s | 1.0×10-7 |
| Inlet mass fraction of A | 0.1 |
| Inlet mass fraction of B | 0.0 |
| Inlet mass fraction of I | 0.9 |
表4 颗粒聚团体系模拟参数设置
Table 4 Parameter of numerical simulation in dense phase
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Particle diameter/m | 1.0×10-4 |
| Grid size/m | 1.0×10-5~5.0×10-5 |
| Time step/s | 1.0×10-7 |
| Inlet mass fraction of A | 0.1 |
| Inlet mass fraction of B | 0.0 |
| Inlet mass fraction of I | 0.9 |
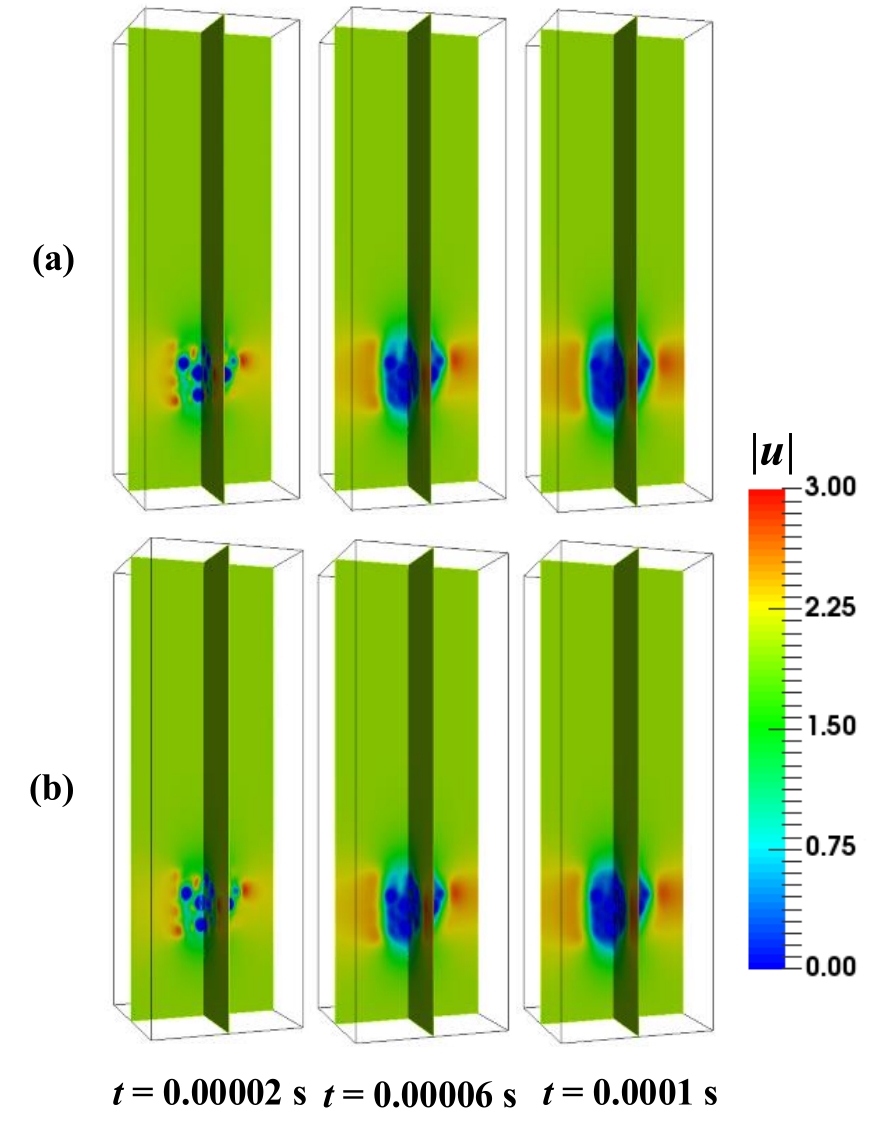
图11 颗粒聚团体系内气相速度分布(Res=10):(a) 实心球形颗粒;(b) 中空多孔颗粒
Fig.11 Velocity distributions in particle cluster system (Res=10): (a) solid spherical particle; (b) hollow porous particle
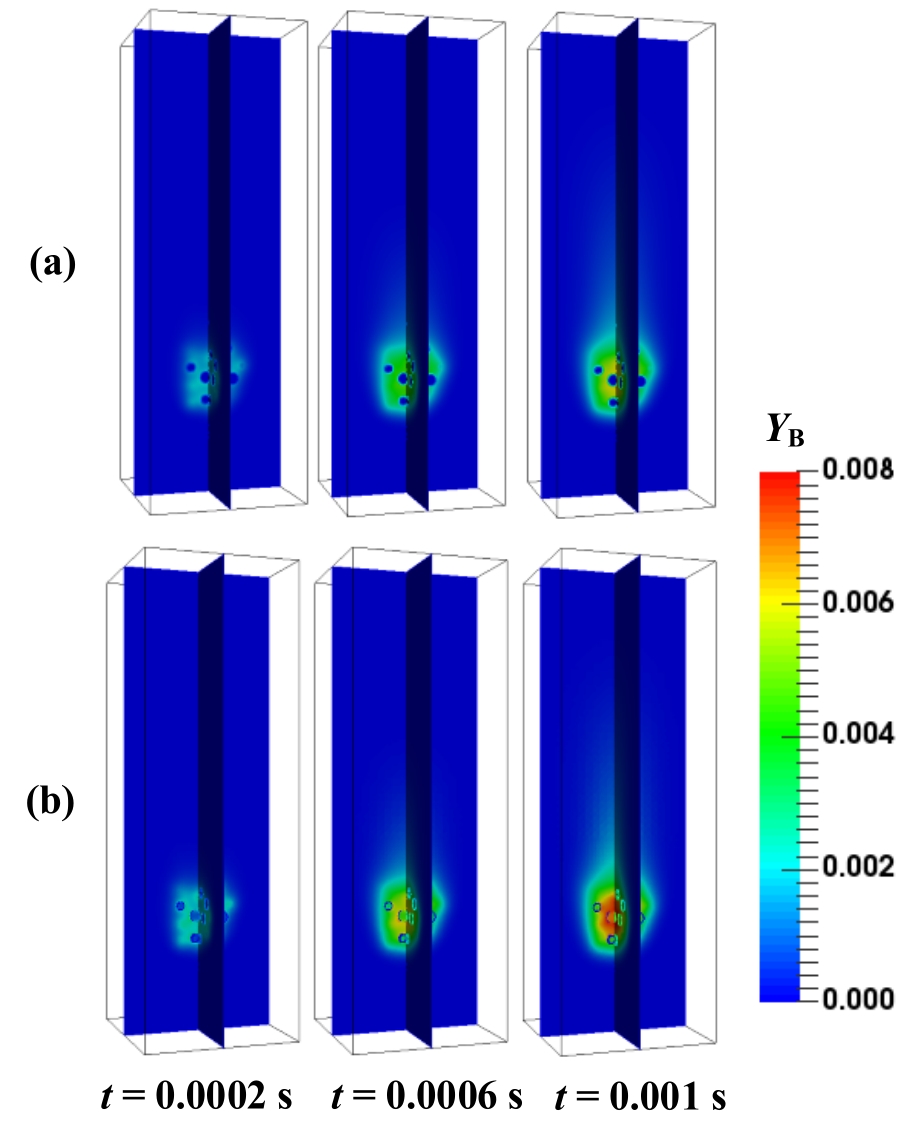
图12 颗粒聚团体系中产物B的质量分数分布(Res=10):(a) 实心球形颗粒;(b) 中空多孔颗粒
Fig.12 The mass fractions of product B in particle cluster system (Res=10): (a) solid spherical particle; (b) hollow porous particle
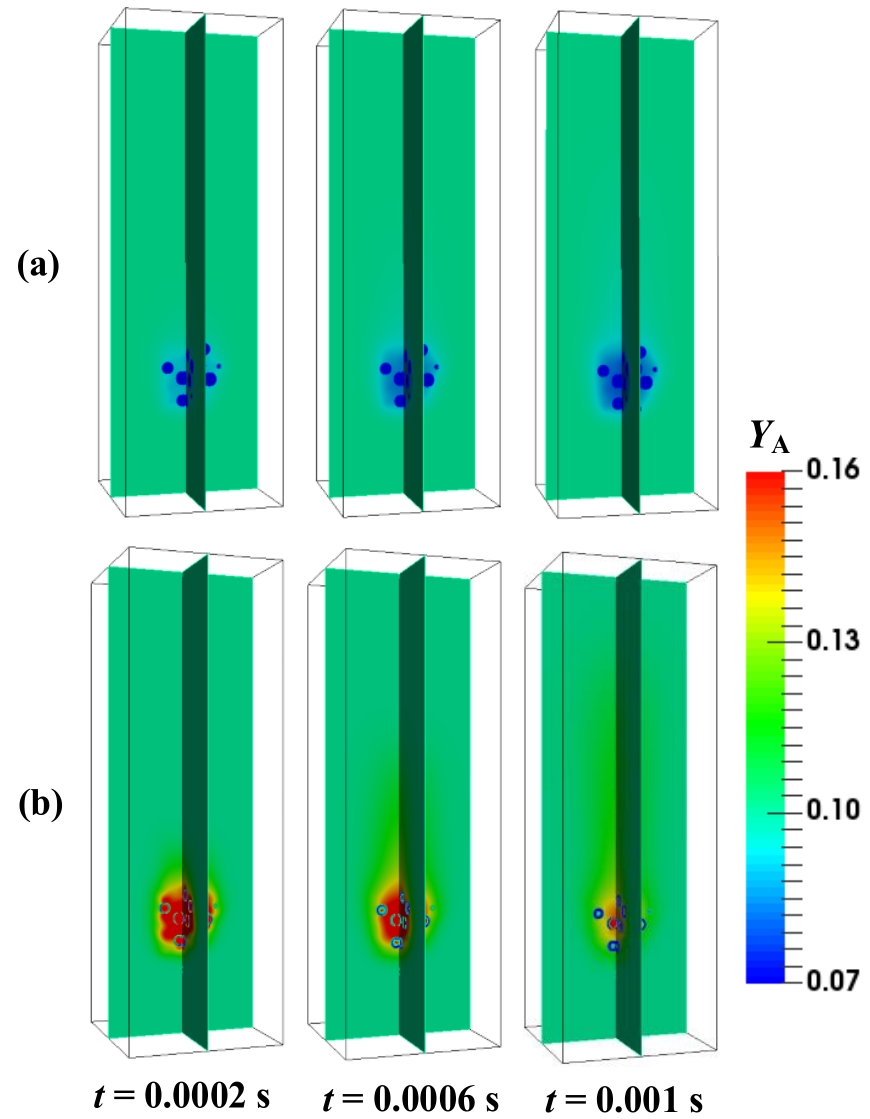
图13 颗粒聚团体系中气体A的质量分数分布(Res=10):(a) 实心球形颗粒;(b) 中空多孔颗粒
Fig.13 The mass fractions of reactant A in particle cluster system (Res=10): (a) solid spherical particle; (b) hollow porous particle
| 1 | 郭慕孙, 李洪钟. 流态化手册 [M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2008: 150-159. |
| Kwauk M, Li H Z. Handbook of fluidization [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2008: 150-159. | |
| 2 | 金涌, 祝京旭, 汪展文. 流态化工程原理 [M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2001: 2-14. |
| Jin Y, Zhu J X, Wang Z W. Fluidization engineering principles [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua Univeristy Press, 2001: 2-14. | |
| 3 | 李洪钟, 郭慕孙. 回眸与展望流态化科学与技术 [J]. 化工学报, 2013, 64(1): 52-60. |
| Li H Z, Kwauk M. Review and prospect of fluidization science and technology [J]. CIESC Journal, 2013, 64(1): 52-60. | |
| 4 | Amjadi O, Tahmasebpoor M. Improving fluidization behavior of cohesive Ca(OH)2 adsorbent using hydrophilic silica nanoparticles: parametric investigation [J]. Particuology, 2018, 40: 52-61. |
| 5 | Kashyap M, Tadiboyina M R, Okolo C, et al. Improving circulating fluidized bed dehydrogenation technology through optimization of fluidization [J]. Particuology, 2020, 50: 127-134. |
| 6 | Yu Y, Zhang C, Zhang Z, et al. Characterizing the catalyst fluidization with field synergy to improve the amine absorption for CO2 capture [J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2019, 27(7): 1608-1617. |
| 7 | Zhou C, Fan X, Duan C, et al. A method to improve fluidization quality in gas-solid fluidized bed for fine coal beneficiation [J]. Particuology, 2019, 43: 181-192. |
| 8 | 李洪钟, 郭慕孙. 气固流态化的散式化 [M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2002: 38-52. |
| Li H Z, Kwauk M. Particulatization of gas-solid fluidization [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002: 38-52. | |
| 9 | Liu B, Zhang X, Wang L, et al. Fluidization of non-spherical particles: sphericity, Zingg factor and other fluidization parameters [J]. Particuology, 2008, 6(2): 125-129. |
| 10 | Hilton J E, Mason L R, Cleary P W. Dynamics of gas-solid fluidised beds with non-spherical particle geometry [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(5): 1584-1596. |
| 11 | Nan W, Wang Y, Wang J. Numerical analysis on the fluidization dynamics of rodlike particles [J]. Advanced Powder Technology, 2016, 27(5): 2265-2276. |
| 12 | Mandø M, Rosendahl L. On the motion of non-spherical particles at high Reynolds number [J]. Powder Technology, 2010, 202(1/2/3): 1-13. |
| 13 | Li X, Visaveliya N, Hafermann L, et al. Hierarchically structured particles for micro flow catalysis [J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 326: 1058-1065. |
| 14 | Cheng Q, Tian Y, Lyu S, et al. Confined small-sized cobalt catalysts stimulate carbon-chain growth reversely by modifying ASF law of Fischer-Tropsch synthesis [J]. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1): 1-9. |
| 15 | Wang X, Li M, Cao C, et al. Surfactant-free palladium nanoparticles encapsulated in ZIF-8 hollow nanospheres for size-selective catalysis in liquid-phase solution [J]. ChemCatChem, 2016, 8(20): 3224-3228. |
| 16 | Yao D, Wang Y, Katherine H L, et al. Balancing effect between adsorption and diffusion on catalytic performance inside hollow nanostructured catalyst [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2019, 9(4): 2969-2976. |
| 17 | 邹海魁, 初广文, 向阳, 等. 超重力反应强化技术最新进展 [J]. 化工学报, 2015, 66(8): 2805-2809. |
| Zou H K, Chu G W, Xiang Y, et al. New progress of HIGEE reaction technology [J]. Journal of Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2015, 66(8): 2805-2809. | |
| 18 | Nakamura H, Tokuda T, Iwasaki T, et al. Numerical analysis of particle mixing in a rotating fluidized bed [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2007, 62(11): 3043-3056. |
| 19 | De Broqueville A, De Wilde J. Numerical investigation of gas-solid heat transfer in rotating fluidized beds in a static geometry [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2009, 64(6): 1232-1248. |
| 20 | De Wilde J, De Broqueville A. Experimental investigation of a rotating fluidized bed in a static geometry [J]. Powder Technology, 2008, 183(3): 426-435. |
| 21 | 威尔特 J R, 威克斯 C E, 威尔逊 R E, 等. 动量、热量和质量传递原理 [M]. 马紫峰, 吴卫生, 译. 第4版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005: 403-463. |
| Welty J R, Wicks C E, Wilson R E, et al. Fundamentals of momentum, heat and mass transfer [M]. Ma Z F, Wu W S, trans. 4th Ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005: 403-463. | |
| 22 | Lu J, Das S, Peters E A J F, et al. Direct numerical simulation of fluid flow and mass transfer in dense fluid-particle systems with surface reactions [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2018, 176: 1-18. |
| 23 | Lu B, Luo H, Li H, et al. Speeding up CFD simulation of fluidized bed reactor for MTO by coupling CRE model [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2016, 143: 341-350. |
| 24 | Carlos Varas A E, Peters E A J F, Kuipers J A M. Computational fluid dynamics-discrete element method (CFD-DEM) study of mass-transfer mechanisms in riser flow [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry, 2017, 56(19): 5558-5572. |
| 25 | Das S, Deen N G, Kuipers J A M. A DNS study of flow and heat transfer through slender fixed-bed reactors randomly packed with spherical particles [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 160: 1-19. |
| 26 | Deen N G, Kuipers J A M. Direct numerical simulation of fluid flow and mass transfer in dense fluid-particle systems [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(33): 11266-11274. |
| 27 | Lu J, Peters E A J F, Kuipers J A M. Direct numerical simulation of fluid flow and mass transfer in particle clusters [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(13): 4664-4679. |
| 28 | Lu J, Peters E A J F, Kuipers J A M. Direct numerical simulation of fluid flow and dependently coupled heat and mass transfer in fluid-particle systems [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 204: 203-219. |
| 29 | Lu J, Tan M D, Peters E A J F, et al. Direct numerical simulation of reactive fluid-particle systems using an immersed boundary method [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2018, 57(45): 15565-15578. |
| 30 | Van Der Hoef M A, Van Sint Annaland M, Deen N G, et al. Numerical simulation of dense gas-solid fluidized beds: a multiscale modeling strategy [J]. Annual Review of Fluid Mechanics, 2008, 40(1): 47-70. |
| 31 | Green D W, Perry R H. Perry's chemical engineers' handbook [M]. 8th Ed. New York: The McGraw-Hill Companies, 2002: 746-755. |
| 32 | Li J, Agarwal R K, Zhou L, et al. Investigation of a bubbling fluidized bed methanation reactor by using CFD-DEM and approximate image processing method [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2019, 207: 1107-1120. |
| 33 | Christoph K, Christoph G, Alice H, et al. Models, algorithms and validation for opensource DEM and CFD-DEM [J]. Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, 2012, 12: 140-152. |
| 34 | Chu K W, Wang B, Xu D L, et al. CFD-DEM simulation of the gas-solid flow in a cyclone separator [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(5): 834-847. |
| 35 | Wu C, Cheng Y, Ding Y, et al. CFD-DEM simulation of gas-solid reacting flows in fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) process [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2010, 65(1): 542-549. |
| 36 | Gidaspow D. Multiphase flow and fluidization: continuum and kinetic theory descriptions [M]. New York: Academic Press, 1994: 421-446. |
| 37 | Tian T, Wang H, Ge W, et al. Detecting particle clusters in particle-fluid systems by a density based method [J]. Communications in Computational Physics, 2019, 26(5): 1617-1630. |
| 38 | Lu B, Zhang J, Luo H, et al. Numerical simulation of scale-up effects of methanol-to-olefins fluidized bed reactors [J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 171: 244-255. |
| 39 | Tian P, Wei Y, Ye M, et al. Methanol to olefins (MTO): from fundamentals to commercialization [J]. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(3): 1922-1938. |
| 40 | Ying L, Yuan X, Ye M, et al. A seven lumped kinetic model for industrial catalyst in DMTO process [J]. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2015, 100: 179-191. |
| 41 | Zhao Y, Li H, Ye M, et al. 3D numerical simulation of a large scale MTO fluidized bed reactor [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013, 52(33): 11354-11364. |
| 42 | Das A K, Baudrez E, Marin G B, et al. Three-dimensional simulation of a fluid catalytic cracking riser reactor [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2003, 42(12): 2602-2617. |
| 43 | Trujillo W R, De Wilde J. Computational fluid dynamics simulation of fluid catalytic cracking in a rotating fluidized bed in a static geometry [J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(11): 5288-5298. |
| [1] | 姜保成 肖涛 王松松 郭学益 王亲猛. 氧枪区位置对大型铜熔炼氧气底吹炉流动特性影响研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2025, 25(2): 150-158. |
| [2] | 张建文 苏国庆 冯磊磊 李彦 张帆 卢世林 赵亚辉 盛刚. 加氢装置高压换热器铵盐结晶行为研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2025, 25(1): 20-33. |
| [3] | 张鑫镝 赵杰 郭建华 张卫义. 下弯管直弯比对新型密排式液-固循环流化床换热器稳定流态化性能的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(9): 1016-1026. |
| [4] | 张蕊 于庆波 娄一荻. 烟气再循环率对水泥回转窑加热过程的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(9): 1027-1035. |
| [5] | 屠楠 王驰宇 刘晓群 刘家琛 方嘉宾. 多级挡板对横流鼓泡床颗粒停留时间分布影响的数值模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(9): 1047-1057. |
| [6] | 陈简一 许闽 仝仓 黄彩凤 淮秀兰. 基于CFD-DEM的新型挡板式移动床反应器内Ca(OH)2/CaO热化学储能过程模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(8): 894-903. |
| [7] | 尹孝辉 刘辉 嵇翔宇 独家卿 王瑞 胡磊. 马氏体相变对CMT熔覆9Cr-1Mo涂层残余应力影响的数值模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(8): 926-936. |
| [8] | 张明 孙欢 王强强 陈家庆 尚超 李想 王春升 孔令真. 管式旋流气液分离器流场特性与分离性能研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(7): 772-782. |
| [9] | 邢谷雨 袁俊飞 王林 江河 冯梓城 王梦轩. 矩形周期性扩缩微通道内沸腾流动与传热[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(7): 793-804. |
| [10] | 陆彪 王行银 胡青云 陈燕 陈德敏 高靖. 富氧燃烧条件对加热炉板坯加热过程的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(7): 805-814. |
| [11] | 杨婷 董亚超 都健. 基于卷积神经网络的偶联反应催化剂及速率常数预测方法[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(7): 833-842. |
| [12] | 孙祎 钱付平 于灵涛 吴越 黄乃金 吴昊. 回转式换热器换热元件换热及阻力特性的数值研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(6): 670-680. |
| [13] | 莫畏难 苏有勇 朱冬冬. 低管径比固定床反应器床层特性及流动传热模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(6): 692-704. |
| [14] | 张馨艺 徐宁文 李小明 王树众. 辅助气淬风优化熔渣离心粒化特性数值模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(5): 523-532. |
| [15] | 赵阳 谢明辉 向家伟 刘肖肖 李帅亮 吕世军 吴亮 周国忠 张庆华 杨超. 不同桨型组合淤浆聚合釜内固液悬浮特性研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(4): 403-413. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||