

过程工程学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (7): 794-806.DOI: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.220204CSTR: 32067.14.jproeng.220204
张智霖1( ), 丁磊1,2(
), 丁磊1,2( ), 周强1, 余剑1, 郭昌进1, 张德伟2,3
), 周强1, 余剑1, 郭昌进1, 张德伟2,3
收稿日期:2020-06-28
修回日期:2020-09-01
出版日期:2021-07-28
发布日期:2021-07-27
通讯作者:
丁磊 zhangzhilin1211@163.com;dinglei1978@163.com
作者简介:张智霖(1996-),男,安徽省马鞍山市人,硕士研究生,市政工程专业,E-mail: zhangzhilin1211@163.com基金资助:
Zhilin ZHANG1( ), Lei DING1,2(
), Lei DING1,2( ), Qiang ZHOU1, Jian YU1, Changjin GUO1, Dewei ZHANG2,3
), Qiang ZHOU1, Jian YU1, Changjin GUO1, Dewei ZHANG2,3
Received:2020-06-28
Revised:2020-09-01
Online:2021-07-28
Published:2021-07-27
Contact:
Lei DING zhangzhilin1211@163.com;dinglei1978@163.com
摘要:
以木薯酒精厂生产过程中产生的脱水污泥为原料,采用响应曲面法 Box-Behnken模型优化了木薯酒精污泥基活性炭的制备工艺,同时对最优成品进行一系列表征分析,并将其应用于没食子酸废水的处理研究。活性炭的最优制备条件为活化温度489℃,浸渍时间14 h,活化时间51 min,氯化锌浓度21.53%,该条件下样品的碘吸附值达521.64 mg/g。表征分析显示其表面布有众多孔壁较薄、大小不一的孔洞,金属含量较小,BET比表面积达441.86 m2/g,平均孔径为2.50 nm,拥有丰富的微孔结构,表面富有较多的含氧官能团。考察了活性炭投加量、pH、接触时间、溶液温度对样品去除水中没食子酸的影响。结果表明,样品能够高效去除没食子酸,且随着投加量的增加和pH值降低,没食子酸的去除率呈增长趋势。木薯酒精污泥基活性炭对没食子酸的吸附符合pseudo second-order动力学模型和Freundlich等温模型,最大吸附量为126.72 mg/g。扩散机理显示除颗粒内扩散外也包含液膜扩散过程。热力学分析表明该吸附反应是自发进行的吸热且熵增的过程。本研究将为制备高性能污泥活性炭并应用于高浓度天然有机物废水处理提供理论基础。
中图分类号:
张智霖, 丁磊, 周强, 余剑, 郭昌进, 张德伟. 响应曲面法优化木薯酒精污泥基活性炭制备及对没食子酸的吸附性能[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(7): 794-806.
Zhilin ZHANG, Lei DING, Qiang ZHOU, Jian YU, Changjin GUO, Dewei ZHANG. Optimization of preparation of cassava alcohol sludge-based activated carbon by response surface methodology and its adsorption properties for gallic acid[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2021, 21(7): 794-806.
| Factor | Code | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Activation temperature/℃ | A | 400 | 500 | 600 |
| Impregnation time/h | B | 6 | 12 | 18 |
| Activation time/min | C | 30 | 60 | 90 |
| Zinc chloride concentration/% | D | 10 | 20 | 30 |
表1 Box-Behnken实验设计的自变量水平和编码值
Table 1 Independent variable levels and codified values for the Box-Behnken experimental design
| Factor | Code | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| Activation temperature/℃ | A | 400 | 500 | 600 |
| Impregnation time/h | B | 6 | 12 | 18 |
| Activation time/min | C | 30 | 60 | 90 |
| Zinc chloride concentration/% | D | 10 | 20 | 30 |
| Run | Activation temperature/℃, A | Impregnation time/min, B | Activation time/min, C | Zinc chloride concentration/%, D | Iodine values, R/(mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | Predict | |||||
| 1 | 500 | 12 | 90 | 10 | 490.21 | 490.45 |
| 2 | 500 | 6 | 60 | 30 | 503.17 | 503.89 |
| 3 | 500 | 12 | 60 | 20 | 525.24 | 521.49 |
| 4 | 500 | 6 | 90 | 20 | 506.38 | 503.06 |
| 5 | 500 | 12 | 90 | 30 | 447.16 | 456.53 |
| 6 | 400 | 18 | 60 | 20 | 493.57 | 490.82 |
| 7 | 400 | 12 | 30 | 20 | 454.21 | 465.91 |
| 8 | 500 | 18 | 90 | 20 | 472.93 | 478.86 |
| 9 | 500 | 18 | 30 | 20 | 515.08 | 516.46 |
| 10 | 400 | 12 | 60 | 10 | 470.93 | 468.77 |
| 11 | 500 | 12 | 60 | 20 | 515.63 | 521.49 |
| 12 | 500 | 18 | 60 | 30 | 502.18 | 493.55 |
| 13 | 500 | 6 | 60 | 10 | 480.93 | 491.19 |
| 14 | 600 | 18 | 60 | 20 | 458.98 | 462.14 |
| 15 | 400 | 6 | 60 | 20 | 492.63 | 489.8 |
| 16 | 500 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 502.60 | 494.74 |
| 17 | 500 | 12 | 30 | 30 | 508.62 | 508.69 |
| 18 | 600 | 12 | 60 | 30 | 445.74 | 445.95 |
| 19 | 400 | 12 | 90 | 20 | 484.65 | 482.49 |
| 20 | 500 | 18 | 60 | 10 | 498.15 | 499.05 |
| 21 | 600 | 12 | 90 | 20 | 434.93 | 424.85 |
| 22 | 600 | 12 | 30 | 20 | 466.93 | 470.71 |
| 23 | 600 | 12 | 60 | 10 | 447.05 | 446.89 |
| 24 | 500 | 12 | 30 | 10 | 476.64 | 467.57 |
| 25 | 400 | 12 | 60 | 30 | 478.70 | 476.91 |
| 26 | 500 | 12 | 60 | 20 | 518.76 | 521.49 |
| 27 | 600 | 6 | 60 | 20 | 462.58 | 465.64 |
| 28 | 500 | 12 | 60 | 20 | 527.47 | 521.49 |
| 29 | 500 | 12 | 60 | 20 | 520.36 | 521.49 |
表2 Box-Behnken实验设计结果与实验及预测值
Table 2 Experimental Box-Behnken design matrix and measured and predicted results
| Run | Activation temperature/℃, A | Impregnation time/min, B | Activation time/min, C | Zinc chloride concentration/%, D | Iodine values, R/(mg/g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Experiment | Predict | |||||
| 1 | 500 | 12 | 90 | 10 | 490.21 | 490.45 |
| 2 | 500 | 6 | 60 | 30 | 503.17 | 503.89 |
| 3 | 500 | 12 | 60 | 20 | 525.24 | 521.49 |
| 4 | 500 | 6 | 90 | 20 | 506.38 | 503.06 |
| 5 | 500 | 12 | 90 | 30 | 447.16 | 456.53 |
| 6 | 400 | 18 | 60 | 20 | 493.57 | 490.82 |
| 7 | 400 | 12 | 30 | 20 | 454.21 | 465.91 |
| 8 | 500 | 18 | 90 | 20 | 472.93 | 478.86 |
| 9 | 500 | 18 | 30 | 20 | 515.08 | 516.46 |
| 10 | 400 | 12 | 60 | 10 | 470.93 | 468.77 |
| 11 | 500 | 12 | 60 | 20 | 515.63 | 521.49 |
| 12 | 500 | 18 | 60 | 30 | 502.18 | 493.55 |
| 13 | 500 | 6 | 60 | 10 | 480.93 | 491.19 |
| 14 | 600 | 18 | 60 | 20 | 458.98 | 462.14 |
| 15 | 400 | 6 | 60 | 20 | 492.63 | 489.8 |
| 16 | 500 | 6 | 30 | 20 | 502.60 | 494.74 |
| 17 | 500 | 12 | 30 | 30 | 508.62 | 508.69 |
| 18 | 600 | 12 | 60 | 30 | 445.74 | 445.95 |
| 19 | 400 | 12 | 90 | 20 | 484.65 | 482.49 |
| 20 | 500 | 18 | 60 | 10 | 498.15 | 499.05 |
| 21 | 600 | 12 | 90 | 20 | 434.93 | 424.85 |
| 22 | 600 | 12 | 30 | 20 | 466.93 | 470.71 |
| 23 | 600 | 12 | 60 | 10 | 447.05 | 446.89 |
| 24 | 500 | 12 | 30 | 10 | 476.64 | 467.57 |
| 25 | 400 | 12 | 60 | 30 | 478.70 | 476.91 |
| 26 | 500 | 12 | 60 | 20 | 518.76 | 521.49 |
| 27 | 600 | 6 | 60 | 20 | 462.58 | 465.64 |
| 28 | 500 | 12 | 60 | 20 | 527.47 | 521.49 |
| 29 | 500 | 12 | 60 | 20 | 520.36 | 521.49 |
| Std. Dev. | Mean | C.V./% | PRESS | R2 | Adj R2 | Pred R2 | Adeq precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.81 | 486.29 | 1.61 | 4529.62 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 17.20 |
表3 回归模型方程的标准差和R2分析结果
Table 3 Standard deviation and R2 for the regression model equation
| Std. Dev. | Mean | C.V./% | PRESS | R2 | Adj R2 | Pred R2 | Adeq precision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7.81 | 486.29 | 1.61 | 4529.62 | 0.96 | 0.91 | 0.77 | 17.20 |
| Source | Sum of squares | Degree of freedom | Mean square | F | Prob>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 18880.62 | 14 | 1348.62 | 22.11 | <0.0001 |
| A | 2093.10 | 1 | 2093.10 | 34.31 | <0.0001 |
| B | 4.56 | 1 | 4.56 | 0.075 | 0.7885 |
| C | 642.89 | 1 | 642.89 | 10.54 | 0.0059 |
| D | 39.05 | 1 | 39.05 | 0.64 | 0.4370 |
| AB | 5.15 | 1 | 5.15 | 0.084 | 0.7757 |
| AC | 974.59 | 1 | 974.59 | 15.98 | 0.0013 |
| AD | 20.59 | 1 | 20.59 | 0.34 | 0.5705 |
| BC | 527.28 | 1 | 527.28 | 8.64 | 0.0108 |
| BD | 82.93 | 1 | 82.93 | 1.36 | 0.2631 |
| CD | 1407.71 | 1 | 1407.71 | 23.08 | 0.0003 |
| A2 | 10819.05 | 1 | 10819.05 | 177.34 | < 0.0001 |
| B2 | 81.88 | 1 | 81.88 | 1.34 | 0.2660 |
| C2 | 2506.94 | 1 | 2506.94 | 41.09 | < 0.0001 |
| D2 | 2865.11 | 1 | 2865.11 | 46.96 | < 0.0001 |
| Residual | 854.08 | 14 | 61.01 | ||
| Lack of fit | 761.20 | 10 | 76.12 | 3.28 | 0.1319 |
| Pure error | 92.89 | 4 | 23.22 | ||
| Cor total | 19734.70 | 28 | |||
表4 拟合模型和模型参数的方差分析统计
Table 4 ANOVA statistics for the fitted model and parameters in the model
| Source | Sum of squares | Degree of freedom | Mean square | F | Prob>F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | 18880.62 | 14 | 1348.62 | 22.11 | <0.0001 |
| A | 2093.10 | 1 | 2093.10 | 34.31 | <0.0001 |
| B | 4.56 | 1 | 4.56 | 0.075 | 0.7885 |
| C | 642.89 | 1 | 642.89 | 10.54 | 0.0059 |
| D | 39.05 | 1 | 39.05 | 0.64 | 0.4370 |
| AB | 5.15 | 1 | 5.15 | 0.084 | 0.7757 |
| AC | 974.59 | 1 | 974.59 | 15.98 | 0.0013 |
| AD | 20.59 | 1 | 20.59 | 0.34 | 0.5705 |
| BC | 527.28 | 1 | 527.28 | 8.64 | 0.0108 |
| BD | 82.93 | 1 | 82.93 | 1.36 | 0.2631 |
| CD | 1407.71 | 1 | 1407.71 | 23.08 | 0.0003 |
| A2 | 10819.05 | 1 | 10819.05 | 177.34 | < 0.0001 |
| B2 | 81.88 | 1 | 81.88 | 1.34 | 0.2660 |
| C2 | 2506.94 | 1 | 2506.94 | 41.09 | < 0.0001 |
| D2 | 2865.11 | 1 | 2865.11 | 46.96 | < 0.0001 |
| Residual | 854.08 | 14 | 61.01 | ||
| Lack of fit | 761.20 | 10 | 76.12 | 3.28 | 0.1319 |
| Pure error | 92.89 | 4 | 23.22 | ||
| Cor total | 19734.70 | 28 | |||
| Sample | SBET/(m2/g) | SMicro/(m2/g) | VTotal/ (cm3/g) | VMicro/(cm3/g) | Daver/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASAC | 441.86 | 299.76 | 0.276 | 0.155 | 2.50 |
表5 CASAC的比表面积及孔结构
Table 5 Structural information of CASAC
| Sample | SBET/(m2/g) | SMicro/(m2/g) | VTotal/ (cm3/g) | VMicro/(cm3/g) | Daver/nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASAC | 441.86 | 299.76 | 0.276 | 0.155 | 2.50 |
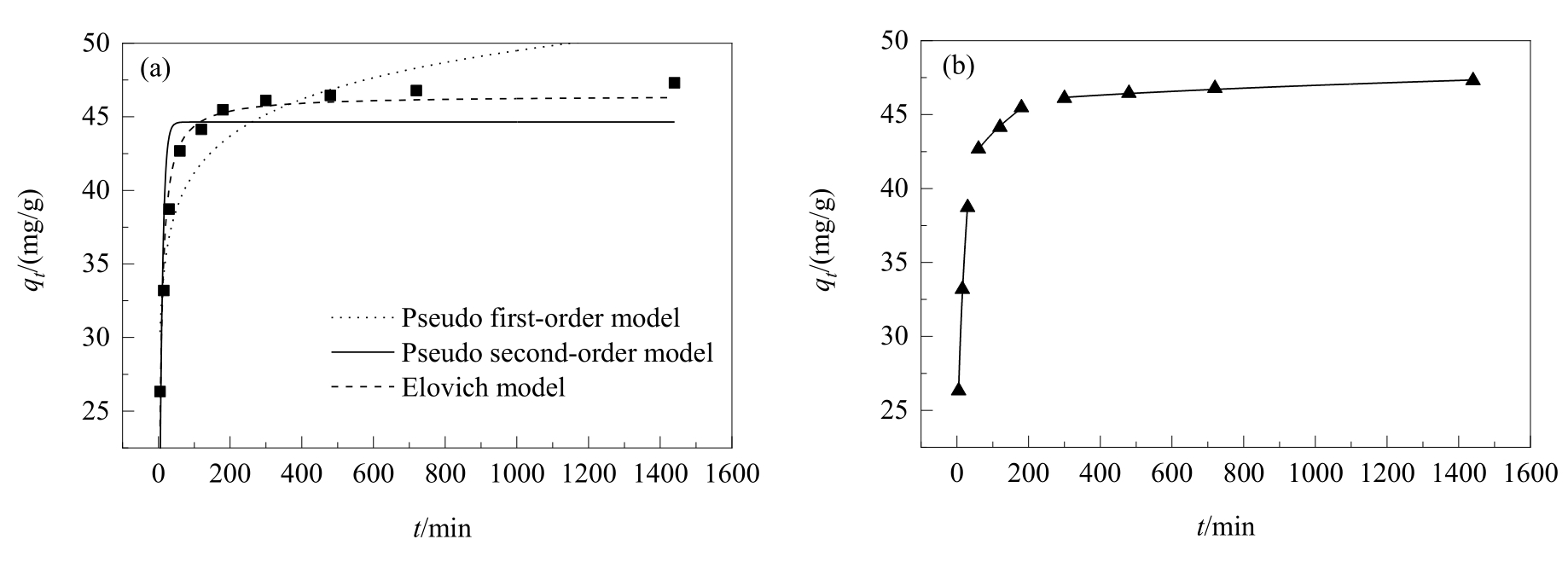
图8 (a) GA在CASAC上的吸附动力学拟合曲线及(b) CASAC吸附GA的颗粒内扩散模型
Fig.8 (a) The fitted curves of adsorption kinetics of GA on CASAC and (b) intra-particle diffusion models for GA on CASAC
| Sample | Pseudo first-order model | Pseudo second-order model | Elovich model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | R2 | k2/[g/(mg·min)] | R2 | R2 | |||
| CASAC | 0.127 | 0.777 | 0.005 | 0.966 | 3243.449 | 0.277 | 0.867 |
表6 GA在CASAC的吸附动力学参数
Table 6 Kinetic parameter of GA adsorption on CASAC
| Sample | Pseudo first-order model | Pseudo second-order model | Elovich model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k1/min-1 | R2 | k2/[g/(mg·min)] | R2 | R2 | |||
| CASAC | 0.127 | 0.777 | 0.005 | 0.966 | 3243.449 | 0.277 | 0.867 |
| Sample | Intra-particle diffusion | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | R2 | R2 | |||||||
| CASAC | 3.825 | 17.973 | 0.997 | 0.490 | 38.856 | 0.998 | 0.057 | 45.171 | 0.988 |
表7 GA在CASAC上的颗粒内扩散模型拟合参数
Table 7 Parameters of intra-particle diffusion model for GA adsorption on CASAC
| Sample | Intra-particle diffusion | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | R2 | R2 | |||||||
| CASAC | 3.825 | 17.973 | 0.997 | 0.490 | 38.856 | 0.998 | 0.057 | 45.171 | 0.988 |
| Sample | Temperature/K | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | qm/(mg/g) | R2 | K2 | 1/n | R2 | ||
| CASAC | 298 | 0.207 | 107.819 | 0.955 | 29.895 | 0.251 | 0.967 |
| 308 | 0.202 | 115.487 | 0.961 | 31.164 | 0.259 | 0.967 | |
| 318 | 0.242 | 117.591 | 0.961 | 34.192 | 0.247 | 0.965 | |
表8 CASAC对GA的吸附等温线模型拟合参数
Table 8 Parameters of the adsorption isotherm model for GA on CASAC
| Sample | Temperature/K | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K1 | qm/(mg/g) | R2 | K2 | 1/n | R2 | ||
| CASAC | 298 | 0.207 | 107.819 | 0.955 | 29.895 | 0.251 | 0.967 |
| 308 | 0.202 | 115.487 | 0.961 | 31.164 | 0.259 | 0.967 | |
| 318 | 0.242 | 117.591 | 0.961 | 34.192 | 0.247 | 0.965 | |
| Sample | T/K | ΔG/(kJ/mol) | ΔH/(kJ/mol) | ΔS/[J/(mol·K)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASAC | 298 | -10.37 | 9.78 | 67.62 |
| 308 | -11.05 | |||
| 318 | -11.73 |
表9 吸附热力学模型参数
Table 9 Adsorption thermodynamic parameters
| Sample | T/K | ΔG/(kJ/mol) | ΔH/(kJ/mol) | ΔS/[J/(mol·K)] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASAC | 298 | -10.37 | 9.78 | 67.62 |
| 308 | -11.05 | |||
| 318 | -11.73 |
| 1 | Wu Y, Xia X, Dong S, et al. Industrial scale extraction and stripping devices for continuous recovery of gallic acid from Chinese nutgall processing wastewater [J]. Environmental Engineering Research, 2017, 22(3): 288-293. |
| 2 | Celestino G G, Henriques R R, Shiguihara A L, et al. Adsorption of gallic acid on nanoclay modified with poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(28): 28444-28454. |
| 3 | 杨德敏, 夏宏, 袁建梅. 臭氧氧化法处理焦化废水生化出水的反应动力学 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2014, 8(1): 32-37. |
| Yang D M, Xia H, Yuan J M. Reaction kinetics of biological treatment of coking wastewater by ozonation [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2014, 8(1): 32-37. | |
| 4 | 李文君, 王成章. 微生物降解没食子酸生产焦性没食子酸的研究进展 [J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2015, 21(3): 226-231. |
| Li W J, Wang C Z. Advance on degrading gallic acid to pyrogallic acid applying microorganism [J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2015, 21(3): 226-231. | |
| 5 | Panizza M, Cerisola G. Electrochemical degradation of gallic acid on a BDD anode [J]. Chemosphere, 2009, 77(8): 1060-1064. |
| 6 | 张军杰, 刘娜, 高原, 等. 分子印迹磁性纳米材料对石榴皮中没食子酸的选择性富集和检测 [J]. 分析实验室, 2020, 39(5): 566-571. |
| Zhang J J, Liu N, Gao Y, et al. Molecularly imprinted magnetic nanomaterials for selective enrichment and detection of gallic acid in pomegranate rind [J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory, 2020, 39(5): 566-571. | |
| 7 | 徐超, 刘金鑫, 孙伟之, 等. 新型超高交联吸附树脂的制备及其对水杨酸、没食子酸吸附性能 [J]. 环境化学, 2018, 37(4): 807-816. |
| Xu C, Liu J X, Sun W Z, et al. Synthesis of novel hypercrosslinked resin and their absorption towards salicylic acid and gallic acid [J]. Environmental Chemistry, 2018, 37(4): 807-816. | |
| 8 | Wong S, Yac'cob N A N, Ngadi N, et al. From pollutant to solution of wastewater pollution: synthesis of activated carbon from textile sludge for dye adsorption [J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2018, 26(4): 870-878. |
| 9 | Silva C P, Jaria G, Otero M, et al. Adsorption of pharmaceuticals from biologically treated municipal wastewater using paper mill sludge-based activated carbon [J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2019, 26(13): 13173-13184. |
| 10 | 邓凤霞, 邱珊, 岳秀丽, 等. 非均相催化臭氧氧化深度处理炼油废水 [J]. 浙江大学学报(工学版), 2015, 49(3): 555-563. |
| Deng F X, Qiu S, Yue X L, et al. Advanced treatment of refinery wastewater by heterogeneous catalytic ozonation [J]. Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science), 2015, 49(3): 555-563. | |
| 11 | Kacan E. Optimum BET surface areas for activated carbon produced from textile sewage sludges and its application as dye removal [J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2016, 166: 116-123 |
| 12 | 鞠振宇. 木薯酒精废水治理工艺研究 [C]//《环境工程》2018年全国学术年会论文集(下册). 北京: 《环境工程》编辑部, 2018: 293-295. |
| Ju Z Y. Study on treatment of cassava alcohol wastewater [C]//Proceedings of the 2018 national academic conference on environmental engineering (volume 2), Beijing: Editorial Office of Environmental Engineering, 2018: 293-295. | |
| 13 | 夏晨娇, 周宗远, 何锐. 木薯酒精废水的深度处理工程实例 [J]. 环境科技, 2016, 29(4): 46-49. |
| Xia C J, Zhou Z Y, He R. Engineering example of advanced treatment of cassava alcohol wastewater [J]. Environmental Science and Technology, 2016, 29(4): 46-49. | |
| 14 | Herath G A D, Poh L S, Ng W J. Statistical optimization of glyphosate adsorption by biochar and activated carbon with response surface methodology [J]. Chemosphere, 2019, 227: 533-540. |
| 15 | 狄军贞, 赵微, 朱志涛, 等. 响应曲面法优化强化混凝工艺处理微污染水 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(1): 27-32. |
| Di J Z, Zhao W, Zhu Z T, et al. Treatment of response surface methodology to optimize enhanced coagulation process for micro-polluted water [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(1): 27-32. | |
| 16 | Ferreira S L C, Bruns R E, Ferreira H S, et al. Box-Behnken design: an alternative for the optimization of analytical methods [J]. Analytica Chimica Acta, 2007, 597(2): 179-186. |
| 17 | 靳晓鹏. 木薯污泥活性炭的制备及对六价铬的吸附研究 [D]. 马鞍山: 安徽工业大学, 2018: 18-19, 26-29. |
| Jin X P. Preparation of cassava sludged-based activated carbon and study on hexavalent chromium adsorption [D]. Ma'anshan: Anhui Univercity of Technology, 2018: 18-19, 26-29. | |
| 18 | 朱云华. MIEX树脂去除水源中没食子酸的特性与机理研究 [D]. 马鞍山: 安徽工业大学, 2016: 30-31. |
| Zhu Y H. The removal mechanism of gallic acid in source water by MIEX resin [D]. Ma'anshan: Anhui Univercity of Technology, 2016: 30-31. | |
| 19 | 程松, 张利波, 夏洪应, 等. 响应曲面法优化CO2活化制备夏威夷坚果壳基活性炭 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2015, 9(9): 4495-4502. |
| Cheng S, Zhang L B, Xia H Y. Preparation of activated carbon from Hawaii nut shell via CO2 activation using response surface methodology [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2015, 9(9): 4495-4502. | |
| 20 | Ding L, Jin X, Gao Y, et al. Removal of Cr(VI) from suddenly polluted raw water using MIEX resin parameters of optimization [J]. Fresenius Environmental Bulleti, 2019, 28(7): 5052-5060. |
| 21 | 范世锁, 李慧, 张浩, 等. 响应面优化污泥-茶渣生物炭的制备 [J]. 环境工程学报, 2017, 11(3): 1778-1786. |
| Fan S S, Li H, Zhang H, et al. Application of response surface methodology for the optimization of biochar preparation derived from sludge and tea residue [J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2017, 11(3): 1778-1786. | |
| 22 | Esfandiar N, Nasernejad B, Ebadi T. Removal of Mn(II) from groundwater by sugarcane bagasse and activated carbon (a comparative study): application of response surface methodology (RSM) [J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry 2014, 20(5): 3726-3736. |
| 23 | 贾韫翰, 丁磊, 任培月, 等. 基于响应曲面法的磁性离子交换树脂去除甲基橙和刚果红的优化 [J]. 过程工程学报, 2020, 20(9): 1035-1044. |
| Jia Y H, Ding L, Ren P Y, et al. Removal optimization of methyl orange and Congo red adsorbed on MIEX resin using response surface methodology [J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2020, 20(9): 1035-1044. | |
| 24 | 牛志睿, 刘羽, 李大海, 等. 响应面法优化制备污泥基活性炭 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2014, 34(12): 3022-3029. |
| Niu Z R, Liu Y, Li D H, et al. Optimization of sludge-based activated carbon preparation using response surface methodology [J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2014, 34(12): 3022-3029. | |
| 25 | Özdemir M, Bolgaz T, Saka C, et al. Preparation and characterization of activated carbon from cotton stalks in a two-stage process [J]. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 2011, 92(1): 171-175. |
| 26 | You Y, Zhang X, Li P, et al. Co-production of xylooligosaccharides and activated carbons from Camellia oleifera shell treated by the catalysis and activation of zinc chloride [J]. Bioresource Technology, 2020, 306: 123131. |
| 27 | 吴东强, 马培勇, 胡淞, 等. 污泥-锯末混合ZnCl2活化制备活性炭 [J]. 过程工程学报, 2018, 18(4): 792-798. |
| Wu D Q, Ma P Y, Hu S, et al. Preparation of activated carbon from sludge and sawdust with ZnCl2 as activator [J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2018, 18(4): 792-798. | |
| 28 | Shoaib A G M, El-Sikaily A, El Nemr A, et al. Preparation and characterization of highly surface area activated carbons followed type IV from marine red alga (Pterocladia capillacea) by zinc chloride activation [J]. Biomass Conversion and Biorefinery, 2020, DOI: 10.1007/s13399-020-00760-8 . |
| 29 | Jin M, Hu B, Tang X N, et al. Effect of zinc chloride on the sludge carbon-based adsorbent in diesel desulfurization [J]. Earth and Environmental Science, 2020, 446: 032055. |
| 30 | Duan X L, Yuan C G, Jing T T, et al. Removal of elemental mercury using large surface area micro-porous corn cob activated carbon by zinc chloride activation [J]. Fuel, 2019, 239: 830-840. |
| 31 | Qi Y F, Yue Q Y, Han S X, et al. Preparation and mechanism of ultra-lightweight ceramics produced from sewage sludge [J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 176(1/2/3): 76-84. |
| 32 | 杨奇亮, 吴平霄. 改性多孔生物炭的制备及其对水中四环素的吸附性能研究 [J]. 环境科学学报, 2019, 39(12): 3973-3984. |
| Yang Q L, Wu P X. Preparation of modified porous biochar and its adsorption properties for tertracycline in water [J]. Acta Science Circumstantiae, 2019, 39(12): 3973-3984. |
| [1] | 刘家俊 张国范. 微细粒蛇纹石浮选夹带行为与机制研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2025, 25(2): 190-200. |
| [2] | 张继欢 张晋玮 武文龙 林嗣强 李燕 丁磊. 碳酸氢钠改性生物炭的制备及其吸附水中卡马西平的机理分析[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(9): 1106-1119. |
| [3] | 邱明俊 李小敏 尚华 杨江峰 李晋平. 基于低浓度甲烷富集的变压吸附工艺流程优化模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(8): 884-893. |
| [4] | 陈寿天宝 张凯 许振良 程亮 徐孙杰 魏永明. 电子级HEA制备中痕量钠钾离子吸附及过程模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(7): 843-851. |
| [5] | 童佳琪 田景坤 王奕涵 姚鑫 李哲阳 谢峰 吴彩斌 曾桂生 徐今冬. 响应曲面法优化磁铁矿-石英体系瓷球磨矿参数[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(6): 726-733. |
| [6] | 张胜东 华中宝 赵瑜 谢贤 童雄. 响应曲面法优化某磷矿正-反浮选试验研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(5): 546-557. |
| [7] | 汪前雨 张玉明 崔彦斌. 磁性活性炭制备及其在水处理中的研究进展[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(3): 259-272. |
| [8] | 谭雅婕 胡宪伟 杨酉坚 刘爱民 石忠宁 汤帅 王兆文. 氟化氢在氧化铝表面吸附机理的Al8O12团簇模型量子化学计算[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(2): 218-226. |
| [9] | 向波 刘晨明 曹仁强 段锋 李玉平. 大孔树脂对镍钴萃取废水中有机物的吸附性能[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(2): 227-237. |
| [10] | 刘旭东 李玉然 彭书雯 刘利 徐文青 朱廷钰. 高炉煤气中H2S在羟基氧化铁上的吸附氧化机理研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(12): 1417-1424. |
| [11] | 许丽 耿娜 刘文 田京雷 朱廷钰 姚明水 郭旸旸. 含硫烟气对MFM-136捕集CO2的影响及烟气组分共吸附机理研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(12): 1425-1434. |
| [12] | 胡义明 曹阳 黄洋 杨诚 高翔鹏 李明阳. 二胺类药剂对霓石絮凝沉降性能的影响及吸附机理研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(11): 1318-1325. |
| [13] | 徐颖 姚鑫毅 宋永红 孙一平 邹晶晶 郭春彬. 煤气化渣改性工艺及吸附Cd2+性能[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(1): 47-57. |
| [14] | 殷慧卿 武少杰 李明阳 龙红明 王松月 邱志新 高翔鹏. CCS-DETA凝胶球的制备及其对甲基橙的吸附性能[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(4): 590-601. |
| [15] | 王思栋 王留洋 冯雪 张松平 张万忠 罗坚. 静电耦合亲和层析纯化人血清白蛋白的研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(11): 1599-1607. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||