

过程工程学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (7): 836-846.DOI: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.220175CSTR: 32067.14.jproeng.220175
收稿日期:2020-06-08
修回日期:2020-09-03
出版日期:2021-07-28
发布日期:2021-07-27
通讯作者:
田国才 1609488137@qq.com;tiangc01@163.com
作者简介:李小亮(1993-),男,江西省吉安市人,硕士研究生,冶金工程专业,E-mail: 1609488137@qq.com基金资助:
Xiaoliang LI1,2( ), Guocai TIAN1,2(
), Guocai TIAN1,2( )
)
Received:2020-06-08
Revised:2020-09-03
Online:2021-07-28
Published:2021-07-27
Contact:
Guocai TIAN 1609488137@qq.com;tiangc01@163.com
摘要:
采用第一性原理对盐酸在黄铜矿表面不同位点的吸附及反应机理进行研究。结果表明,黄铜矿(001)-S表面重构后形成了二硫化物S22-。盐酸以解离形式在黄铜矿的(001)硫终止面(001)-S上吸附,浸出过程中H+在黄铜矿(001)-S表面上S位点的吸附都会破坏黄铜矿表面所形成的S22-。Cl-的吸附对黄铜矿(001)-S表面结构也会造成一定的破坏,吸附过程中H+和Cl-与黄铜矿表面发生化学反应生成了FeCl2和H2S,这些都有利于黄铜矿的浸出。
中图分类号:
李小亮, 田国才. 盐酸在黄铜矿表面吸附机制的第一性原理计算[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(7): 836-846.
Xiaoliang LI, Guocai TIAN. First-principles calculation of adsorption mechanism of hydrochloric acid on chalcopyrite surface[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2021, 21(7): 836-846.
| Parameter | This work | PWscf[ | VASP[ | Siesta[ | Experimental values[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a=b | 0.5256 | 0.5263 | 0.5279 | 0.5277 | 0.5289 |
| c | 1.0395 | 1.0362 | 1.0364 | 1.0447 | 1.0423 |
| Fe-S | 0.2229 | 0.2241 | 0.2257 | 0.2250 | 0.2257 |
| Cu-S | 0.2307 | 0.2293 | 0.2287 | 0.2300 | 0.2302 |
| Fe-Fe | 0.3696 | 0.3693 | - | - | 0.3713 |
| Cu-Cu | 0.3696 | 0.3693 | - | - | 0.3713 |
| Fe-Cu | 0.3716 | 0.3721 | - | - | 0.3740 |
| S-S | 0.3622 | 0.3659 | - | - | 0.3685 |
表1 优化后黄铜矿体相的几何参数 (nm)
Table 1 Geometrical parameters of the chalcopyrite bulk after optimized
| Parameter | This work | PWscf[ | VASP[ | Siesta[ | Experimental values[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a=b | 0.5256 | 0.5263 | 0.5279 | 0.5277 | 0.5289 |
| c | 1.0395 | 1.0362 | 1.0364 | 1.0447 | 1.0423 |
| Fe-S | 0.2229 | 0.2241 | 0.2257 | 0.2250 | 0.2257 |
| Cu-S | 0.2307 | 0.2293 | 0.2287 | 0.2300 | 0.2302 |
| Fe-Fe | 0.3696 | 0.3693 | - | - | 0.3713 |
| Cu-Cu | 0.3696 | 0.3693 | - | - | 0.3713 |
| Fe-Cu | 0.3716 | 0.3721 | - | - | 0.3740 |
| S-S | 0.3622 | 0.3659 | - | - | 0.3685 |
| Parameter | This work | Siesta[ | VASP[ | PWscf[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-S | 0.220 | 0.223 | 0.2242 | 0.2158 |
| Fe-S | 0.214 | 0.224 | 0.2182 | 0.2319 |
| Cu-S | 0.235 | 0.230 | 0.2359 | 0.2326 |
表2 重构的黄铜矿(001)-S表面(单位为nm) (nm)
Table 2 Reconstructed chalcopyrite (001)-S surface
| Parameter | This work | Siesta[ | VASP[ | PWscf[ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S-S | 0.220 | 0.223 | 0.2242 | 0.2158 |
| Fe-S | 0.214 | 0.224 | 0.2182 | 0.2319 |
| Cu-S | 0.235 | 0.230 | 0.2359 | 0.2326 |
| Adsorption site for H+ | ΔΕ/(kcal/mol) | Distance of Fe-Cl/nm | Siesta[ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -19.4 | 0.232 | -19.2 |
| 2 | -19.5 | 0.231 | -19.3 |
| 3 | -14.4 | 0.227 | -14.5 |
| 4 | -12.8 | 0.230 | -11.9 |
| 5 | -20.9 | 0.230 | -21.2 |
| 6 | -20.0 | 0.232 | -21.0 |
| 7 | -13.5 | 0.230 | -14.6 |
| 8 | -10.6 | 0.229 | - |
表3 盐酸在解离情况下H+在不同吸附位点的吸附能和Fe-Cl键长
Table 3 The adsorption energy and Fe-Cl bond length considering different adsorption sites for H+ in the dissociation of hydrochloric acid
| Adsorption site for H+ | ΔΕ/(kcal/mol) | Distance of Fe-Cl/nm | Siesta[ |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | -19.4 | 0.232 | -19.2 |
| 2 | -19.5 | 0.231 | -19.3 |
| 3 | -14.4 | 0.227 | -14.5 |
| 4 | -12.8 | 0.230 | -11.9 |
| 5 | -20.9 | 0.230 | -21.2 |
| 6 | -20.0 | 0.232 | -21.0 |
| 7 | -13.5 | 0.230 | -14.6 |
| 8 | -10.6 | 0.229 | - |
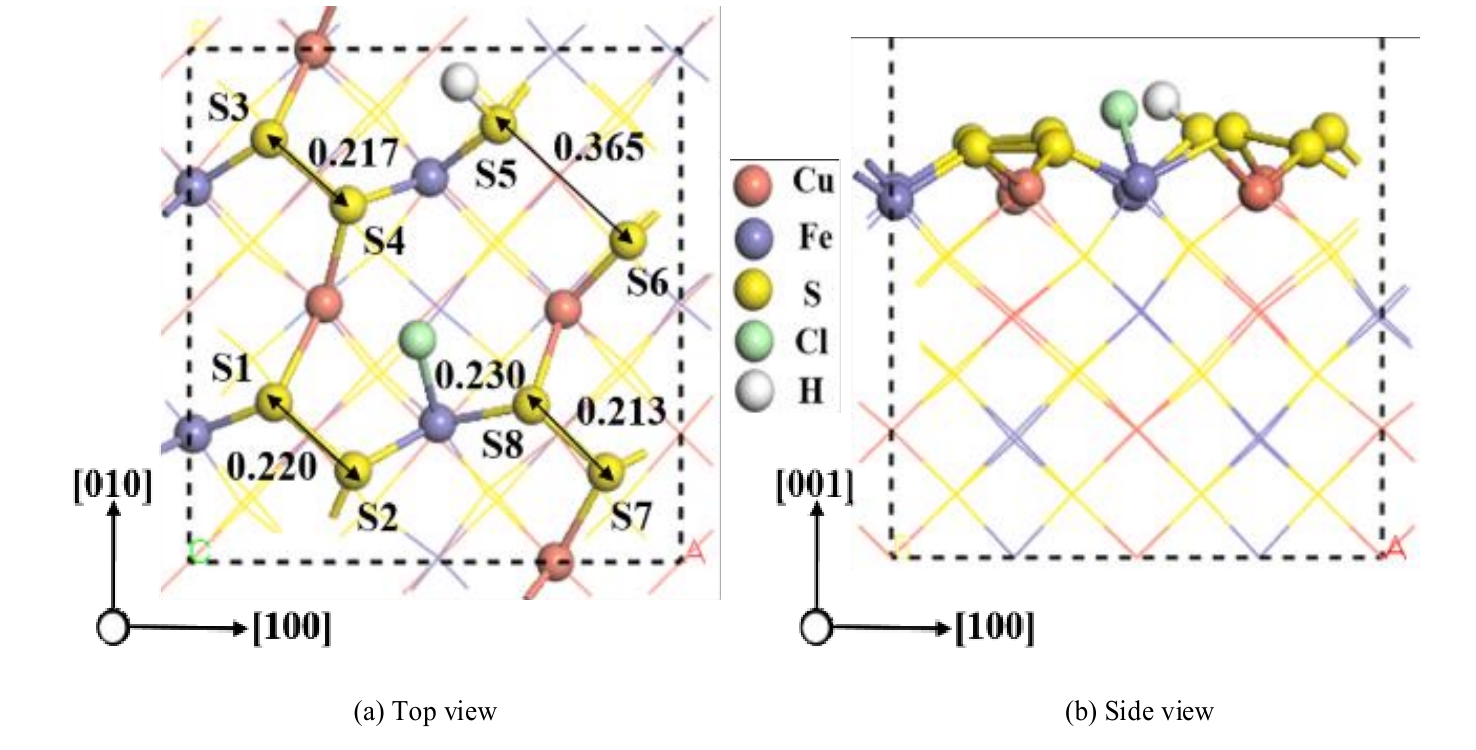
图7 盐酸以解离形式吸附在黄铜矿(001)-S表面最稳定的构型(单位:nm)
Fig.7 The most stable configuration with dissociative adsorption of hydrochloric acid on chalcopyrite (001)-S surface (unit: nm)
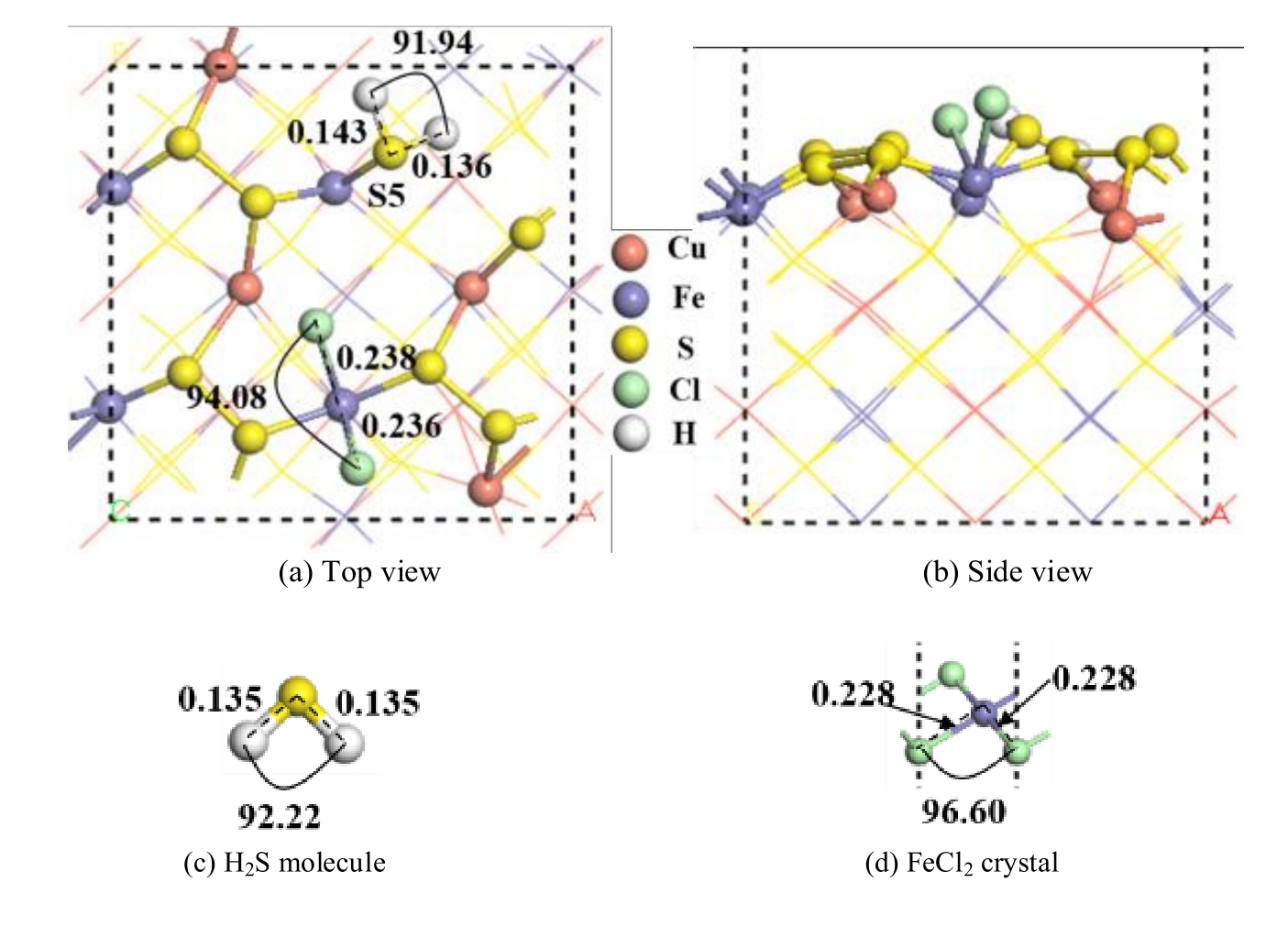
图9 两个盐酸分子解离吸附在黄铜矿(001)-S表面的最稳定构型及优化后的H2S分子和FeCl2晶体(单位为nm)
Fig.9 The most stable configuration of two hydrochloric acid molecules dissociated and adsorbed on chalcopyrite (001)-S surface and H2S molecule and FeCl2 crystal optimized (unit: nm)
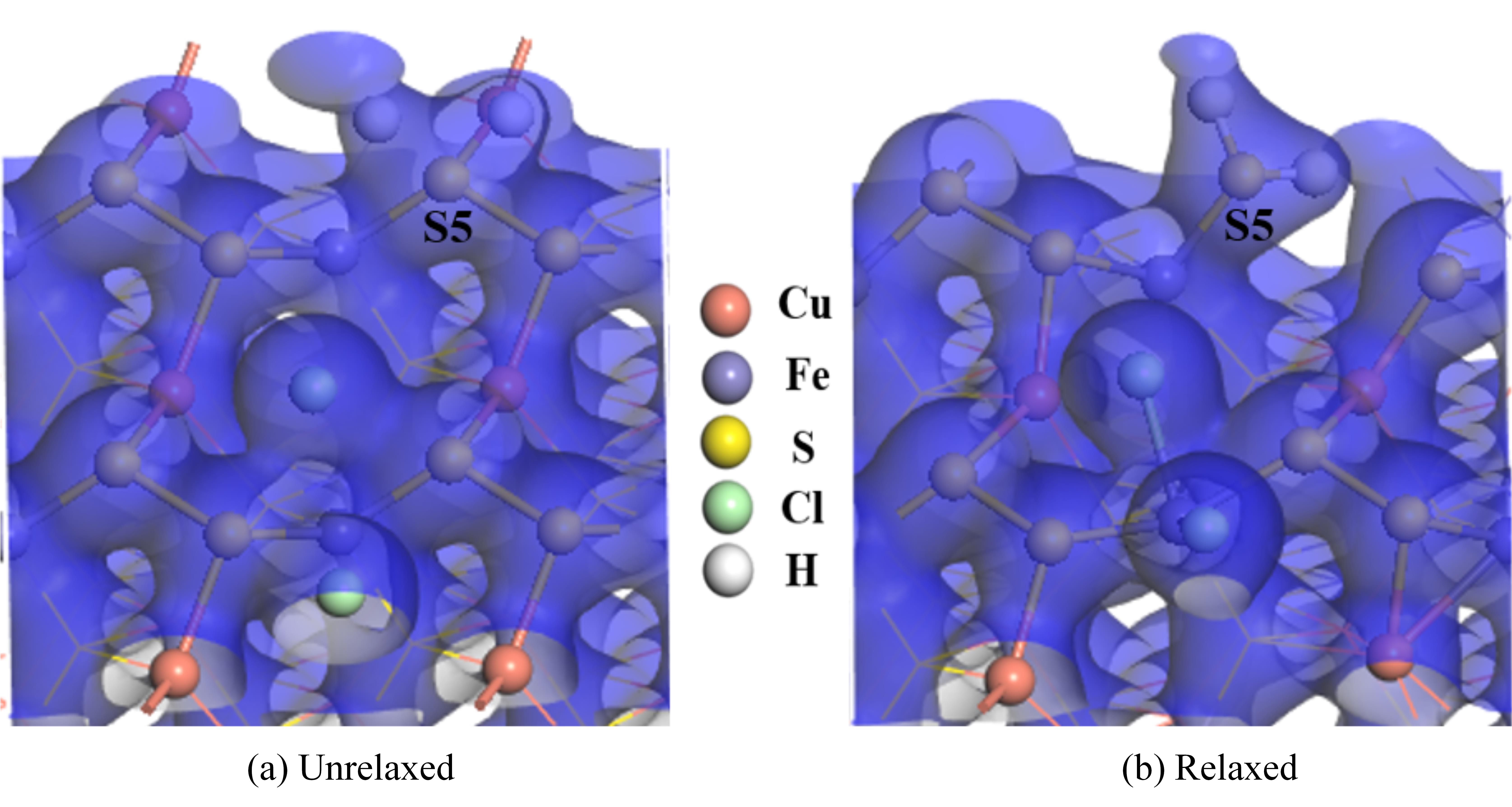
图10 两个盐酸分子解离吸附在黄铜矿(001)-S表面的电子密度图
Fig.10 The electron density of two hydrochloric acid molecules dissociated and adsorbed on chalcopyrite (001)-S surface
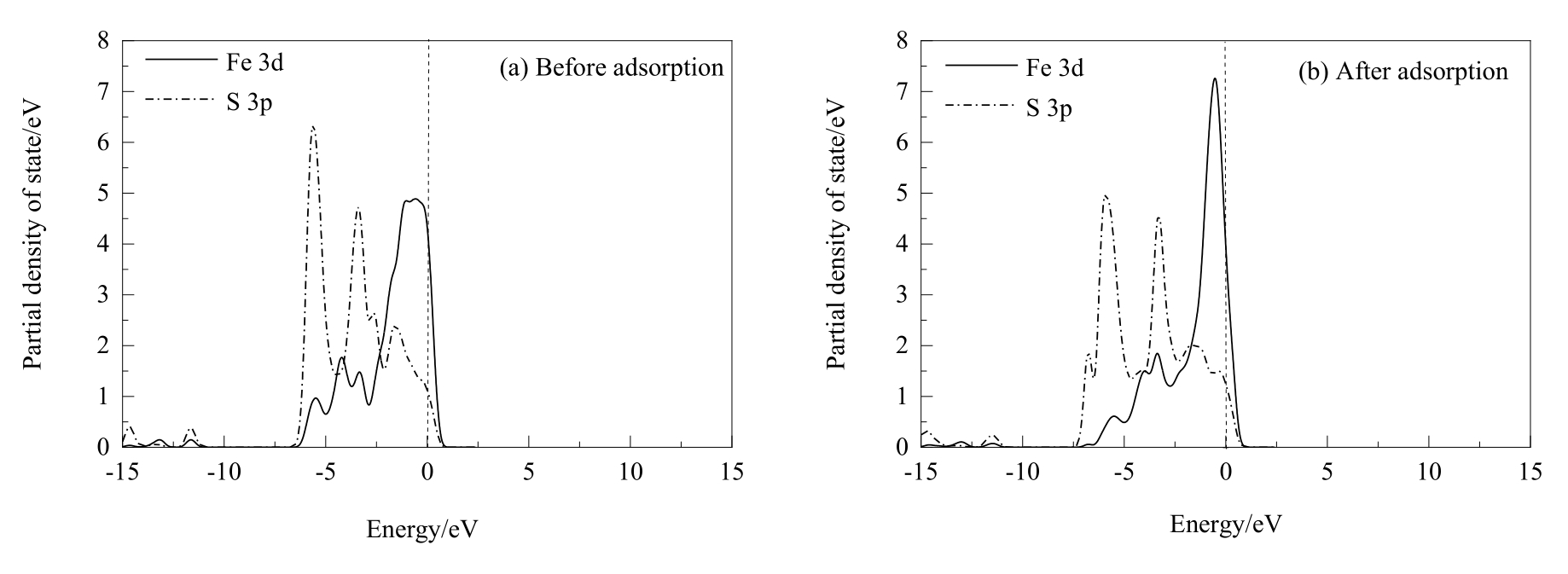
图11 两个盐酸分子解离吸附在黄铜矿(001)-S表面前后Fe和S原子的分态密度分析(虚线表示的是费米能级)
Fig.11 PDOS analysis of Fe and S atoms before and after two hydrochloric acid molecules dissociative adsorption on chalcopyrite (001)-S surface (the dash lines represent Fermi level)
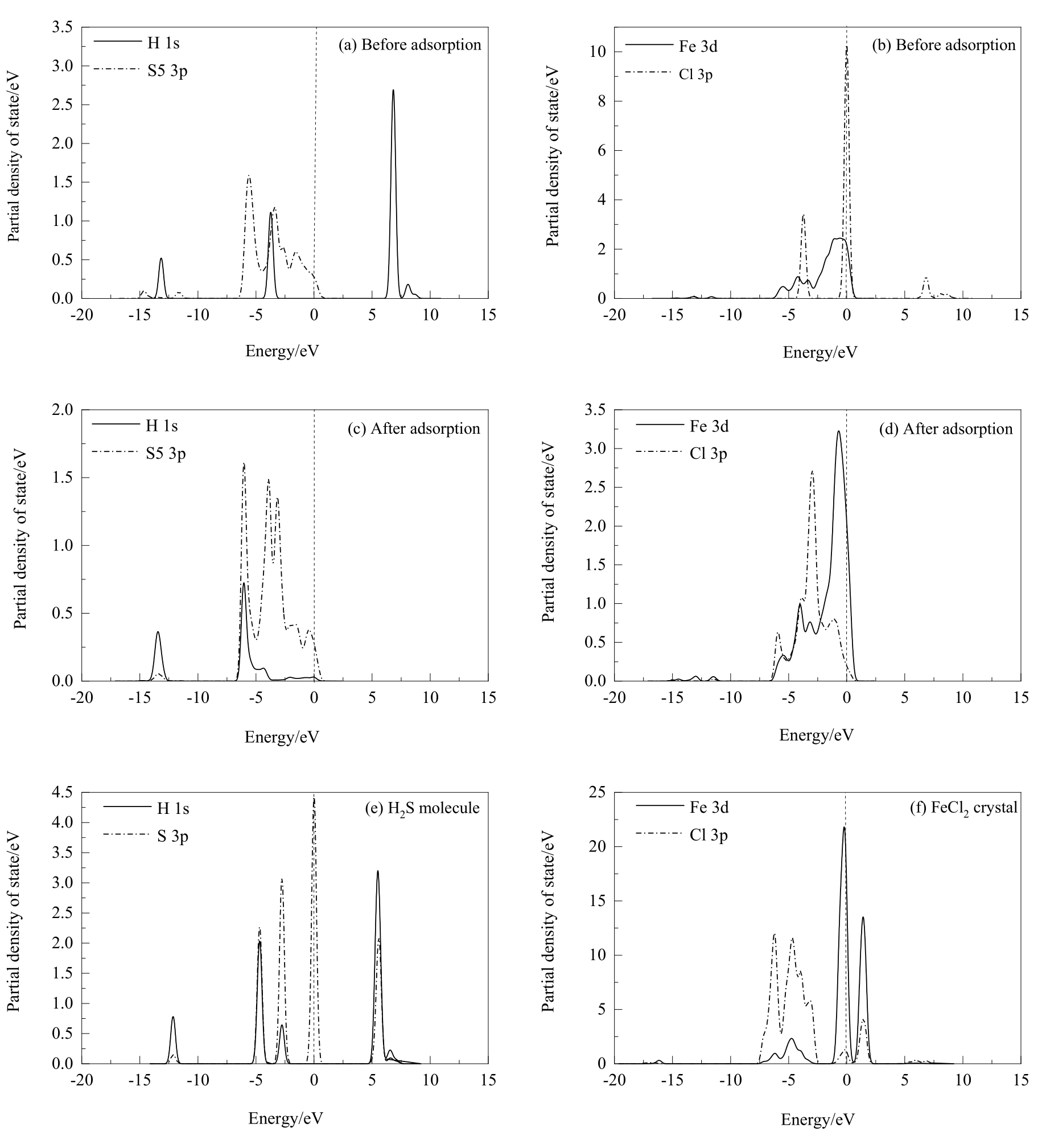
图12 盐酸解离吸附在黄铜矿(001)-S表面前后及优化后的H2S分子和FeCl2晶体的分态密度分析
Fig.12 PDOS analysis of hydrochloric acid before and after dissociative adsorption on chalcopyrite (001)-S surface and the H2S molecule and FeCl2 crystal optimized
| Atom | Adsorption | S orbital, s/e | P orbital, p/e | D orbital, d/e | Total | Charge/e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | Before | 0.66 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.66 | 0.34 |
| H | After | 0.91 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.91 | 0.09 |
| Cl | Before | 1.93 | 5.41 | 0.00 | 7.34 | -0.34 |
| Cl | After | 1.95 | 5.35 | 0.00 | 7.29 | -0.29 |
| S5 | Before | 1.87 | 4.27 | 0.00 | 6.14 | -0.14 |
| S5 | After | 1.85 | 4.38 | 0.00 | 6.23 | -0.23 |
| Fe | Before | 0.36 | 0.50 | 6.94 | 7.79 | 0.21 |
| Fe | After | 0.37 | 0.50 | 6.91 | 7.77 | 0.23 |
表4 盐酸解离吸附在黄铜矿(001)-S表面前后各原子的Mulliken电荷布局
Table 4 Mulliken charge population of atoms before and after dissociative adsorption of hydrochloric acid on chalcopyrite (001)-S surface
| Atom | Adsorption | S orbital, s/e | P orbital, p/e | D orbital, d/e | Total | Charge/e |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H | Before | 0.66 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.66 | 0.34 |
| H | After | 0.91 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.91 | 0.09 |
| Cl | Before | 1.93 | 5.41 | 0.00 | 7.34 | -0.34 |
| Cl | After | 1.95 | 5.35 | 0.00 | 7.29 | -0.29 |
| S5 | Before | 1.87 | 4.27 | 0.00 | 6.14 | -0.14 |
| S5 | After | 1.85 | 4.38 | 0.00 | 6.23 | -0.23 |
| Fe | Before | 0.36 | 0.50 | 6.94 | 7.79 | 0.21 |
| Fe | After | 0.37 | 0.50 | 6.91 | 7.77 | 0.23 |
| 1 | Al-Harahsheh M, Kingman S, Al-Harahsheh A. Ferric chloride leaching of chalcopyrite: synergetic effect of CuCl2 [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 91(1/2/3/4): 89-97. |
| 2 | Córdoba E M, Muñoz J A, Blázquez M L, et al. Leaching of chalcopyrite with ferric ion. part I: general aspects [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 93(3/4): 81-87. |
| 3 | Klauber C. A critical review of the surface chemistry of acidic ferric sulphate dissolution of chalcopyrite with regards to hindered dissolution [J]. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2008, 86(1/2/3/4): 1-17. |
| 4 | Hiroyoshi N, Miki H, Hirajima T, et al. Enhancement of chalcopyrite leaching by ferrous ions in acidic ferric sulfate solutions [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2001, 60(3): 185-197. |
| 5 | Acero P, Cama J, Ayora C. Kinetics of chalcopyrite dissolution at pH=3 [J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2007, 19(2): 173-182. |
| 6 | Li Y, Yao Y, Wang B, et al. New insights into chalcopyrite leaching enhanced by mechanical activation [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 189: 105131-105137. |
| 7 | Córdoba E M, Muñoz J A, Blázquez M L, et al. Leaching of chalcopyrite with ferric ion. part II: effect of redox potential [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2008, 93(3/4): 88-96. |
| 8 | Hackl R P, Dreisinger D B, Peters E, et al. Passivation of chalcopyrite during oxidative leaching in sulfate media [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 1995, 39(1/2/3): 25-48. |
| 9 | Shin D, Ahn J, Lee J. Kinetic study of copper leaching from chalcopyrite concentrate in alkaline glycine solution [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2019, 183: 71-78. |
| 10 | Ruiz M C, Montes K S, Padilla R. Chalcopyrite leaching in sulfate-chloride media at ambient pressure [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 109(1/2): 37-42. |
| 11 | Li J, Kawashima N, Kaplun K, et al. Chalcopyrite leaching: the rate controlling factors [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2010, 74(10): 2881-2893. |
| 12 | Hall S R, Stewart J M. The crystal structure refinement of chalcopyrite, CuFeS2 [J]. Acta Crystallographica Section B: Structural Crystallography and Crystal Chemistry, 1973, 29(3): 579-585. |
| 13 | Harmer S L, Pratt A R, Nesbitt W H, et al. Sulfur species at chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) fracture surfaces [J]. American Mineralogist, 2004, 89(7): 1026-1032. |
| 14 | Klauber C. Fracture-induced reconstruction of a chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) surface [J]. Surface and Interface Analysis, 2003, 35(5): 415-428. |
| 15 | Harmer S L, Thomas J E, Fornasiero D, et al. The evolution of surface layers formed during chalcopyrite leaching [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2006, 70(17): 4392-4402. |
| 16 | Petrovic S J, Bogdanovic G D, Antonijevic M M. Leaching of chalcopyrite with hydrogen peroxide in hydrochloric acid solution [J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2018, 28(7): 1444-1455. |
| 17 | Lu Z Y, Jeffrey M I, Lawson F. An electrochemical study of the effect of chloride ions on the dissolution of chalcopyrite in acidic solutions [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2000, 56(2): 145-155. |
| 18 | Velásquez-Yévenes L, Nicol M, Miki H. The dissolution of chalcopyrite in chloride solutions: part 1: the effect of solution potential [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 103(1/2/3/4): 108-113. |
| 19 | Velásquez-Yévenes L, Miki H, Nicol M. The dissolution of chalcopyrite in chloride solutions: part 2: effect of various parameters on the rate [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 103(1/2/3/4): 80-85. |
| 20 | Nicol M, Miki H, Velásquez-Yévenes L. The dissolution of chalcopyrite in chloride solutions: part 3: mechanisms [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2010, 103(1/2/3/4): 86-95. |
| 21 | Miki H, Nicol M. The dissolution of chalcopyrite in chloride solutions: part IV: the kinetics of the auto-oxidation of copper (I) [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2011, 105(3/4): 246-250. |
| 22 | Watling H R. Chalcopyrite hydrometallurgy at atmospheric pressure: review of acidic chloride process options [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2014, 146: 96-110. |
| 23 | Martínez-Gómez V J, Fuentes-Aceituno J C, Pérez-Garibay R, et al. A study of the electro-assisted reductive leaching of a chalcopyrite concentrate in HCl solutions. part I: kinetic behavior and nature of the chalcopyrite reduction [J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2018, 181: 195-205. |
| 24 | Biegler T. Reduction kinetics of a chalcopyrite electrode surface [J]. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry and Interfacial Electrochemistry, 1977, 85(1): 101-106. |
| 25 | Biegler T, Swift D A. The electrolytic reduction of chalcopyrite in acid solution [J]. Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 1976, 6(3): 229-235. |
| 26 | Tesinsky M, Balaz P. Copper leaching from chalcopyrite: mechanochemical approach [J]. Inżynieria Mineralna, 2017, 18(1): 1-5. |
| 27 | 陈建华, 王进明, 龙贤灏, 等. 硫化铜矿物电子结构的第一性原理研究 [J] 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 42(12): 16-21. |
| Chen J H, Wang J M, Long X H, et al. First-principle theory on electronic structure of copper sulfides [J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2011, 42(12): 16-21. | |
| 28 | de Oliveira C, de Lima G F, de Abreu H A, et al. Reconstruction of the chalcopyrite surfaces: a DFT study [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(10): 6357-6366. |
| 29 | de Lima G F, de Oliveira C, de Abreu H A, et al. Water adsorption on the reconstructed (001) chalcopyrite surfaces [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(21): 10709-10717. |
| 30 | de Lima G F, de Oliveira C, de Abreu H A, et al. Sulfuric and hydrochloric acid adsorption on the reconstructed sulfur terminated (001) chalcopyrite surface [J]. International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 2012, 112(19): 3216-3222. |
| 31 | Perdew J P, Burke K, Ernzerhof M. Generalized gradient approximation made simple [J]. Physical Review Letters, 1996, 77(18): 3865-3868. |
| 32 | de Oliveira C, Duarte H A. Disulphide and metal sulphide formation on the reconstructed (001) surface of chalcopyrite: a DFT study [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2010, 257(4): 1319-1324. |
| 33 | Li K, Zhao Y, Zhang P, et al. Combined DFT and XPS investigation of iodine anions adsorption on the sulfur terminated (001) chalcopyrite surface [J]. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 390: 412-421. |
| 34 | Li Y, Chandra A P, Gerson A R. Scanning photoelectron microscopy studies of freshly fractured chalcopyrite exposed to O2 and H2O [J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 133: 372-386. |
| 35 | Li Y, Kawashima N, Li J, et al. A review of the structure, and fundamental mechanisms and kinetics of the leaching of chalcopyrite [J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 197: 1-3. |
| 36 | Benedek R, Thackeray M M, Low J J, et al. Simulation of aqueous dissolution of lithium manganate spinel from first principles [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2012, 116(6): 4050-4059. |
| 37 | Leung K. First-principles modeling of Mn(II) migration above and dissolution from Li x Mn2O4 (001) surfaces [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2017, 29(6): 2550-2562. |
| 38 | Stack A G, Raiteri P, Gale J D, et al. Accurate rates of the complex mechanisms for growth and dissolution of minerals using a combination of rare-event theories [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(1): 11-14. |
| 39 | Ionescu A, Allouche A, Aycard J P, et al. Study of γ-alumina surface reactivity: adsorption of water and hydrogen sulfide on octahedral aluminum sites [J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2002, 106(36): 9359-9366. |
| 40 | Lectez S, Roques J, Salanne M, et al. Car-Parrinello molecular dynamics study of the uranyl behaviour at the gibbsite/water interface [J]. Journal of Chemical Physics, 2012, 137(15): 154705-154713. |
| [1] | 秦双 方建军 何海洋 邱芝莲 彭礼国 董诗钦. 二氢杨梅素在黄铜矿与方铅矿浮选分离中的作用机理[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(11): 1335-1343. |
| [2] | 吴平平 孟冠华 杜宇 刘宝河 施绪 周瑞 江用彬 章慧娟. CeO2/Bi2WO6 Z型异质结构建及高效催化降解盐酸四环素[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(1): 117-126. |
| [3] | 陶润萍 董伟强 胡庆松 朱靖 王智鑫 徐轶群. Brij30/β-FeOOH/GO复合材料的可控构筑及其对盐酸四环素吸附性能[J]. 过程工程学报, 2022, 22(7): 979-988. |
| [4] | 周育生 邱冠周 景建发 郑富强 王帅 陈凤 郭宇峰. 改性电炉钛渣矿相解构法制备富钛料新工艺研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2022, 22(5): 651-659. |
| [5] | 张亚卓 战金辉. CH3Cl在ZnO(001)和ZnO(100)表面吸附的第一性原理计算[J]. 过程工程学报, 2022, 22(2): 240-248. |
| [6] | 孙帅 孙宏骞 宋静 曲景奎 王勇 齐涛. 动态扩散渗析法回收盐酸的实验与模型分析[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(1): 57-63. |
| [7] | 文康 韦祎 马光辉. 基于响应面法对制备高包埋率ROP-PLGA微球的影响因素分析[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(1): 83-91. |
| [8] | 杨帆 温良英 赵岩 徐健 张生富 杨仲卿. TiO2(100)表面C和Cl2吸附反应的第一性原理计算[J]. 过程工程学报, 2020, 20(5): 569-575. |
| [9] | 李丹 陈德胜 张国之 赵宏欣 齐涛 王伟菁 王丽娜 刘亚辉. 用萃取剂P507从盐酸浸出液中萃取分离钒与铁[J]. 过程工程学报, 2017, 17(6): 1182-1187. |
| [10] | 田国才 胡均贤 字富庭. 氧化剂在黄铜矿氧化浸出中应用的研究进展[J]. 过程工程学报, 2017, 17(4): 664-676. |
| [11] | 肖万海 赵宏欣 宋宁 陈德胜 刘亚辉 王丽娜 齐涛. 钒钛磁铁矿混合精矿在盐酸中Fe/V/Ti的浸出行为[J]. 过程工程学报, 2016, 16(5): 737-743. |
| [12] | 邵大伟 刘亚辉 王伟菁 曹成波 齐涛. 还原焙烧钛渣盐酸浸出过程的动力学[J]. 过程工程学报, 2016, 16(4): 577-583. |
| [13] | 刘鹏飞 张亦飞 游韶玮 薄婧 江小舵. 热酸浸出回收黄钾铁矾渣中有价元素[J]. 过程工程学报, 2016, 16(4): 584-589. |
| [14] | 谢子楠 陈前林 赵丽君. 液膜对不同酸度磷矿浸出液中稀土的提取[J]. , 2013, 13(2): 197-201. |
| [15] | 王宝全 郭强 曲景奎 齐涛. 褐铁型红土矿碱浸渣的常压酸浸工艺条件优化[J]. , 2012, 12(3): 420-426. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||