

过程工程学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 21 ›› Issue (7): 847-856.DOI: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.220221CSTR: 32067.14.jproeng.220221
收稿日期:2020-07-13
修回日期:2020-07-25
出版日期:2021-07-28
发布日期:2021-07-27
通讯作者:
霍锋 tyhu18@ipe.ac.cn;huofeng@ipe.ac.cn
作者简介:胡天媛(1995-),女,安徽省池州市人,硕士研究生,化学工程专业,E-mail: tyhu18@ipe.ac.cn基金资助:
Tianyuan HU1,2( ), Yanlei WANG1, Feng HUO1(
), Yanlei WANG1, Feng HUO1( ), Hongyan HE1
), Hongyan HE1
Received:2020-07-13
Revised:2020-07-25
Online:2021-07-28
Published:2021-07-27
Contact:
Feng HUO tyhu18@ipe.ac.cn;huofeng@ipe.ac.cn
摘要:
离子液体因其优异的物化性质、能抑制多硫化物溶解等特点,近年来被广泛应用于锂硫电池电解液中。在电池充放电产物中,难溶性Li2S和Li2S2易聚集沉积在电极表面,影响电池性能,而目前关于其团聚行为与电解液性质的微观机理研究较少。本工作利用量化计算和分子动力学模拟分析了短链Li2S和Li2S2在离子液体中的微观结构以及形成团簇的情况。通过分析体系的微观结构发现,阳离子中主要与S作用的是侧链甲基,短链多硫化物之间Li-S作用远强于与阴离子的Li-O作用。团簇尺寸分布的结果表明,短链多硫化物在[TFSI]型离子液体中易形成多分子的大团簇,Li2S2体系比Li2S体系中的大团簇比例更高;离子液体阴离子配位能力越强,形成大的Li2S团簇比例越少,但阴离子的构型特点和作用形式也会对团簇的尺寸结构造成影响。
中图分类号:
胡天媛, 王艳磊, 霍锋, 何宏艳. 短链多硫化物在离子液体中聚集行为的分子动力学模拟[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(7): 847-856.
Tianyuan HU, Yanlei WANG, Feng HUO, Hongyan HE. Molecular dynamics simulations of short-chain lithium polysulfides clustering in ionic liquids[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2021, 21(7): 847-856.
| System | Number of ILs | Concentration of Li2S/Li2S2/(mol/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 | ||
| [PP13][TFSI]-Li2S2 | 800 | 49 | 98 | 147 | 196 | 245 |
| [PP13][OTf]-Li2S2 | 800 | 37 | 75 | 112 | 149 | 186 |
| [PP13][TFSI]-Li2S | 800 | 49 | 98 | 147 | 196 | 245 |
| [PP13][OTf]-Li2S | 800 | 37 | 75 | 112 | 149 | 186 |
| [PP13][PF6]-Li2S | 800 | 184 | ||||
| [PP13][DCA]-Li2S | 800 | 163 | ||||
| [PP13]Br-Li2S | 800 | 176 | ||||
表1 模拟体系中各组分数
Table 1 Number of molecules in the simulation systems
| System | Number of ILs | Concentration of Li2S/Li2S2/(mol/L) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.6 | 0.8 | 1.0 | ||
| [PP13][TFSI]-Li2S2 | 800 | 49 | 98 | 147 | 196 | 245 |
| [PP13][OTf]-Li2S2 | 800 | 37 | 75 | 112 | 149 | 186 |
| [PP13][TFSI]-Li2S | 800 | 49 | 98 | 147 | 196 | 245 |
| [PP13][OTf]-Li2S | 800 | 37 | 75 | 112 | 149 | 186 |
| [PP13][PF6]-Li2S | 800 | 184 | ||||
| [PP13][DCA]-Li2S | 800 | 163 | ||||
| [PP13]Br-Li2S | 800 | 176 | ||||
| RILs | Density/(g/cm3) | D+/×10-11 m2/s | D-/×10-11 m2/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| [PP13][TFSI] | 1.38 | 1.843±0.019 | 1.339±0.013 |
| [PP13][OTf] | 1.25 | 1.177±0.012 | 0.734±0.010 |
表2 298 K下MD模拟得到的离子液体密度与自扩散系数
Table 2 Densities and self-diffusion coefficients of ILs at 298 K from MD simulations
| RILs | Density/(g/cm3) | D+/×10-11 m2/s | D-/×10-11 m2/s |
|---|---|---|---|
| [PP13][TFSI] | 1.38 | 1.843±0.019 | 1.339±0.013 |
| [PP13][OTf] | 1.25 | 1.177±0.012 | 0.734±0.010 |
| Angle | θ0/° | Kθ /[kcal/(mol·rad2)] |
|---|---|---|
| Li-S-Li[a] | 138.00 | 55.00 |
| S-Li-S[b] | 60.00 | 218.00 |
| Li-S-Li[b] | 98.00 | 55.00 |
表3 本工作中Li2S和Li2S2的键角参数([a]代表Li2S,[b]代表Li2S2)
Table 3 Angle parameters of Li2S and Li2S2 in this work ([a]for Li2S, [b] for Li2S2)
| Angle | θ0/° | Kθ /[kcal/(mol·rad2)] |
|---|---|---|
| Li-S-Li[a] | 138.00 | 55.00 |
| S-Li-S[b] | 60.00 | 218.00 |
| Li-S-Li[b] | 98.00 | 55.00 |
| Simulation | σLi/×10-1 nm | σS/×10-1 nm | εLi/(kcal/mol) | εS/(kcal/mol) | ρLi2S/(g/cm3) | ρS8/(g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System-1[ | 2.8700 | 3.5500 | 0.0005 | 0.2500 | 1.83 | 1.71 |
| System-2[ | 2.0261 | 3.5640 | 0.0183 | 0.2504 | 1.91 | 1.70 |
| System-3[ | 2.1300 | 3.5500 | 0.0765 | 0.2500 | 1.73 | 1.71 |
| System-4[ | 3.6000 | 3.3032 | 0.0005 | 0.2500 | 1.71 | 1.90 |
| System-5[ | 3.6000 | 3.3900 | 0.0005 | 0.4070 | 1.63 | 1.98 |
| System-6[ | 3.6000 | 3.3900 | 0.0183 | 0.4070 | 1.11 | 1.98 |
表4 LJ参数的模拟(与Li2S和S8的实验密度对比)
Table 4 Force field simulations for LJ parameters (compared with experimental densities of Li2S and S8)
| Simulation | σLi/×10-1 nm | σS/×10-1 nm | εLi/(kcal/mol) | εS/(kcal/mol) | ρLi2S/(g/cm3) | ρS8/(g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| System-1[ | 2.8700 | 3.5500 | 0.0005 | 0.2500 | 1.83 | 1.71 |
| System-2[ | 2.0261 | 3.5640 | 0.0183 | 0.2504 | 1.91 | 1.70 |
| System-3[ | 2.1300 | 3.5500 | 0.0765 | 0.2500 | 1.73 | 1.71 |
| System-4[ | 3.6000 | 3.3032 | 0.0005 | 0.2500 | 1.71 | 1.90 |
| System-5[ | 3.6000 | 3.3900 | 0.0005 | 0.4070 | 1.63 | 1.98 |
| System-6[ | 3.6000 | 3.3900 | 0.0183 | 0.4070 | 1.11 | 1.98 |
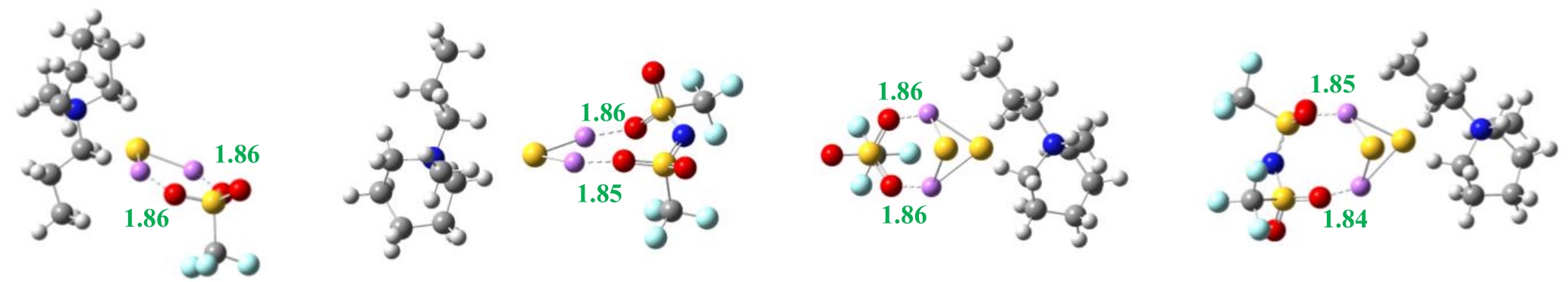
图3 离子对与短链多硫化物作用的最优构型[B3LYP/6-311+g(d,p)水平上](单位:0.1 nm)(a) [PP13][OTf]-Li2S (b) [PP13][TFSI]-Li2S (c) [PP13][OTf]-Li2S2 (d) [PP13][TFSI]-Li2S2
Fig.3 Structures of ion pairs and Li2S/Li2S2 optimized at B3LYP/6-311+g(d,p) level (unit: 0.1 nm)
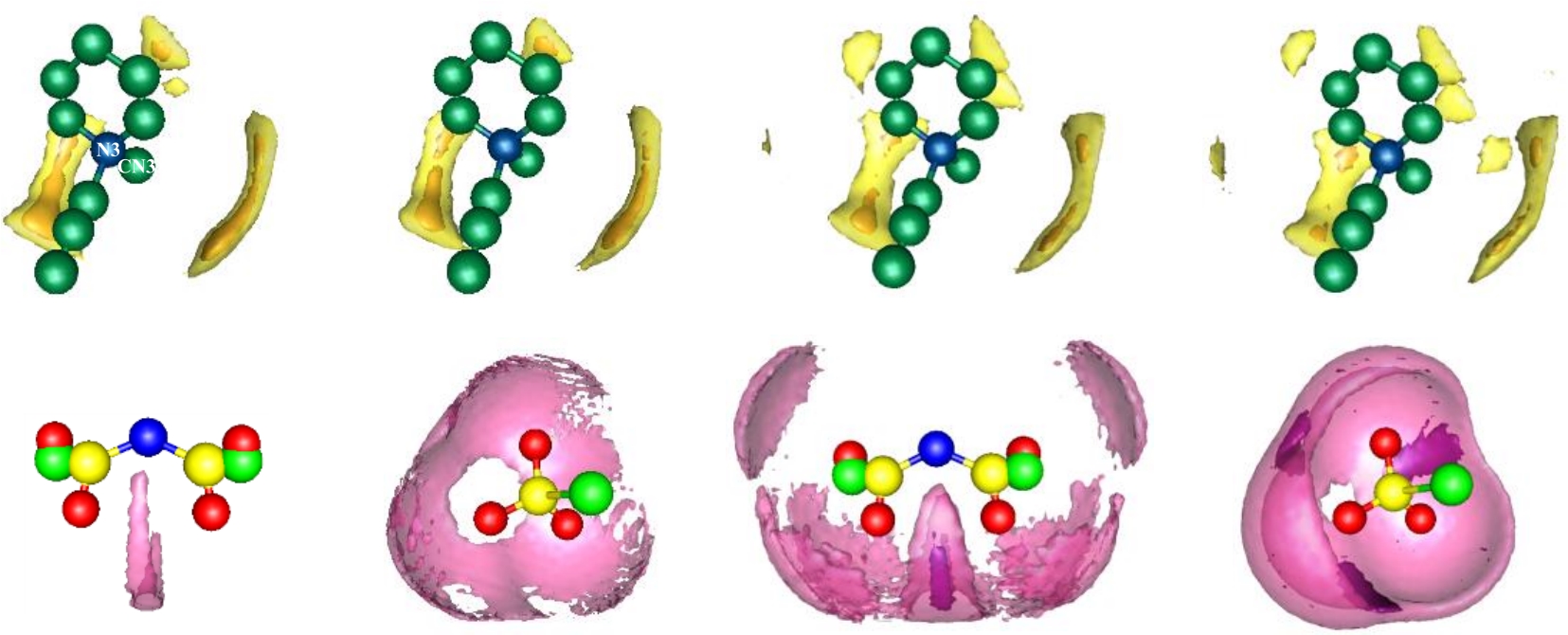
图5 离子液体-短链多硫化物体系中阳离子周围S的SDFs(上栏)和阴离子周围Li的SDFs(下栏)(a) [PP13][TFSI]-Li2S (b) [PP13][OTf]-Li2S (c) [PP13][TFSI]-Li2S2 (d) [PP13][OTf]-Li2S2
Fig.5 SDFs of S around central cations (up panels) and Li around central anions (bottom panels) in ILs and short-chain polysulfides system
| Anion | [PF6]- | [TFSI]- | [OTf]- | [DCA]- | Br- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.91 | 2.91 | 2.41 | 2.10 | 2.65 |
表5 含不同配位能力阴离子的五种离子液体体系中Li2S团簇的平均尺寸
Table 5 The mean size of Li2S clusters in five ILs containing anions with different coordination ability
| Anion | [PF6]- | [TFSI]- | [OTf]- | [DCA]- | Br- |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.91 | 2.91 | 2.41 | 2.10 | 2.65 |
| 1 | Zhu J, Zou J L, Cheng H, et al. High energy batteries based on sulfur cathode [J]. Green Energy & Environment, 2019, 4(4): 345-359. |
| 2 | Pan H, Wei X, Henderson W A, et al. On the way toward understanding solution chemistry of lithium polysulfides for high energy Li-S redox flow batteries [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2015, 5(16): 1500113. |
| 3 | Pan H L, Chen J Z, Cao R G, et al. Non-encapsulation approach for high-performance Li-S batteries through controlled nucleation and growth [J]. Nature Energy, 2017, 2(10): 813-820. |
| 4 | Vijayakumar M, Govind N, Walter E, et al. Molecular structure and stability of dissolved lithium polysulfide species [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(22): 10923-10932. |
| 5 | Barchasz C, Molton F, Duboc C, et al. Lithium/sulfur cell discharge mechanism: an original approach for intermediate species identification [J]. Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 84(9): 3973-3980. |
| 6 | Cuisinier M, Hart C, Balasubramanian M, et al. Radical or not radical: revisiting lithium-sulfur electrochemistry in nonaqueous electrolytes [J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2015, 5(16): 1401801. |
| 7 | Zhang G, Peng H J, Zhao C Z, et al. The radical pathway based on a lithium-metal-compatible high-dielectric electrolyte for lithium-sulfur batteries [J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(51): 16732-16736. |
| 8 | Chu H, Noh H, Kim Y J, et al. Achieving three-dimensional lithium sulfide growth in lithium-sulfur batteries using high-donor-number anions [J]. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 188. |
| 9 | Wang B, Alhassan S M, Pantelides S T. Formation of large polysulfide complexes during the lithium-sulfur battery discharge [J]. Physical Review Applied, 2014, 2(3): 034004. |
| 10 | Yu T, Li F, Liu C Y, et al. Understanding the role of lithium sulfide clusters in lithium-sulfur batteries [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017, 5(19): 9293-9298. |
| 11 | Partovi-Azar P, Kühne T D, Kaghazchi P. Evidence for the existence of Li2S2 clusters in lithium-sulfur batteries: ab initio Raman spectroscopy simulation [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(34): 22009-22014. |
| 12 | Gupta A, Bhargav A, Jones J P, et al. Influence of lithium polysulfide clustering on the kinetics of electrochemical conversion in lithium-sulfur batteries [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2020, 32(5): 2070-2077. |
| 13 | Park C, Ronneburg A, Risse S, et al. Structural and transport properties of Li/S battery electrolytes: role of the polysulfide species [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2019, 123(16): 10167-10177. |
| 14 | Andersen A, Rajput N N, Han K S, et al. Structure and dynamics of polysulfide clusters in a nonaqueous solvent mixture of 1,3-dioxolane and 1,2-dimethoxyethane [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2019, 31(7): 2308-2319. |
| 15 | Xiao J W, Zhou G M, Chen H T, et al. Elaboration of aggregated polysulfide phases: from molecules to large clusters and solid phases [J]. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(10): 7487-7493. |
| 16 | Dong K, Liu X M, Dong H F, et al. Multiscale Studies on Ionic Liquids [J]. Chemical Reviews, 2017, 117(10): 6636-6695. |
| 17 | Zhang L, Dong K, Chen S M, et al. Novel ionic liquid based electrolyte for double layer capacitors with enhanced high potential stability [J]. Science China Chemistry, 2016, 59(5): 547-550. |
| 18 | Plimpton S. Fast parallel algorithms for short-range molecular dynamics [J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1995, 117(1): 1-19. |
| 19 | Zhong X J, Liu Z P, Cao D P. Improved classical united-atom force field for imidazolium-based ionic liquids: tetrafluoroborate, hexafluorophosphate, methylsulfate, trifluoromethylsulfonate, acetate, trifluoroacetate, and bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)amide [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2011, 115(33): 10027-10040. |
| 20 | Jorgensen W L, Maxwell D S, Tirado-Rives J. Development and testing of the OPLS all-atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1996, 118(45): 11225-11236. |
| 21 | Rizzo R C, Jorgensen W L. OPLS all-atom model for amines: resolution of the amine hydration problem [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1999, 121(20): 4827-4836. |
| 22 | Bazito F F C, Kawano Y, Torresi R M. Synthesis and characterization of two ionic liquids with emphasis on their chemical stability towards metallic lithium [J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2007, 52(23): 6427-6437. |
| 23 | Tokuda H, Ishii K, Susan M A B H, et al. Physicochemical properties and structures of room-temperature ionic liquids. 3. variation of cationic structures [J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2006, 110(6): 2833-2839. |
| 24 | Gardas R L, Costa H F, Freire M G, et al. Densities and derived thermodynamic properties of imidazolium-, pyridinium-, pyrrolidinium-, and piperidinium-based ionic liquids [J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2008, 53(3): 805-811. |
| 25 | Liu Z X, Hubble D, Balbuena P B, et al. Adsorption of insoluble polysulfides Li2S x (x=1, 2) on Li2S surfaces [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(14): 9032-9039. |
| 26 | Zou W L, Kalescky R, Kraka E, et al. Relating normal vibrational modes to local vibrational modes with the help of an adiabatic connection scheme [J]. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 2012, 137(8): 084114. |
| 27 | Cornell W D, Cieplak P, Bayly C I, et al. A second generation force field for the simulation of proteins, nucleic acids, and organic molecules [J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1995, 117(19): 5179-5197. |
| 28 | Ou X W, Yu Y Z, Wu R, et al. Shuttle suppression by polymer-sealed graphene-coated polypropylene separator [J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(6): 5534-5542. |
| 29 | Islam M M, Ostadhossein A, Borodin O, et al. ReaxFF molecular dynamics simulations on lithiated sulfur cathode materials [J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(5): 3383-3393. |
| 30 | Pastorino C, Gamba Z. Test of a simple and flexible S8 model molecule in α-S8 crystals [J]. Chemical Physics Letters, 2000, 319(1): 20-26. |
| 31 | Frisch M, Trucks G, Schlegel H B, et al. Gaussian 09 [M]. Revision d. 01. Wallingford, CT: Gaussian Inc., 2009: 28. |
| 32 | Martínez L, Andrade R, Birgin E G, et al. PACKMOL: a package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations [J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2009, 30(13): 2157-2164. |
| 33 | Molinari N, Mailoa J P, Kozinsky B. Effect of salt concentration on ion clustering and transport in polymer solid electrolytes: a molecular dynamics study of PEO-LiTFSI [J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2018, 30(18): 6298-6306. |
| 34 | Schmeisser M, Illner P, Puchta R, et al. Gutmann donor and acceptor numbers for ionic liquids [J]. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2012, 18(35): 10969-10982. |
| [1] | 范俊刚 孟月 赫明鑫 郝家锐 李文秀. COSMO-RS筛选离子液体分离异丙醇-乙腈机理分析[J]. 过程工程学报, 2025, 25(1): 53-61. |
| [2] | 谭雅婕 胡宪伟 杨酉坚 刘爱民 石忠宁 汤帅 王兆文. 氟化氢在氧化铝表面吸附机理的Al8O12团簇模型量子化学计算[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(2): 218-226. |
| [3] | 尹超跃 杨帆 张亲亲 张志刚. 以磷酸酯盐离子液体作为萃取剂萃取精馏分离甲酸乙酯和乙醇共沸物[J]. 过程工程学报, 2024, 24(2): 238-247. |
| [4] | 胡婷婷 刘海建 陈云逸 刘伶俐 戴春爱 韩永生. 锂硫电池中多硫化锂捕获研究进展[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(9): 1231-1243. |
| [5] | 牛典 钱建国 陈健 詹国雄. 基于纳滤-闪蒸的含离子液体废水耦合回收新工艺的评价与分析[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(8): 1220-1230. |
| [6] | 李晴 石萌 郭义敏 何瑞宁 邹昀 童张法. 利用COSMO-RS模型筛选离子液体夹带剂用于水+乙酸体系的分离[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(7): 1063-1072. |
| [7] | 李想 战金辉 许光文. 基于分子动力学模拟研究蒙脱石对油页岩干酪根热解产物分布的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(5): 724-733. |
| [8] | 王凯旋 李涛 李玉 白银鸽 曾少娟 任保增 张香平 董海峰. 超强碱离子液体-有机胺-水复配溶剂高效CO2捕集[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(5): 781-789. |
| [9] | 白烁 王昊 许光文 杨冰冰 康振烨 崔佳瑶 李晨浩 陈庆军 刘艳荣. 离子液体阳离子特性对铂基氧还原电催化剂性能的影响[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(4): 602-615. |
| [10] | 杨晓晴 郑勇 王倩 杨倩 李玉 李涛 任保增. 离子液体中铝的电沉积及精炼[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(3): 396-410. |
| [11] | 宋小龙 王绍康 徐航. 双吡啶含钴离子液体的制备及耦合过硫酸盐催化脱硫[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(12): 1706-1713. |
| [12] | 高瑞斌 易礼鑫 杨子锋 董丽 刘一凡 郭洪范 李雨浓. CO2环加成过程中副产物溴乙醇的催化转化研究[J]. 过程工程学报, 2023, 23(11): 1518-1529. |
| [13] | 马肃 戴毅. 含有偶氮苯结构单元的离子液体在智能材料中的应用与研究进展[J]. 过程工程学报, 2022, 22(8): 1011-1018. |
| [14] | 巨朝阳 余梦婷 雷庭俞 程海翔 任兰会 葛承胜. 密度泛函理论研究金属镧离子的水合团簇[J]. 过程工程学报, 2022, 22(6): 764-773. |
| [15] | 宋春雨 聂普选 马守涛 任国瑜. 典型过程强化技术在纳米材料制备中的应用进展[J]. 过程工程学报, 2021, 21(4): 373-382. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||